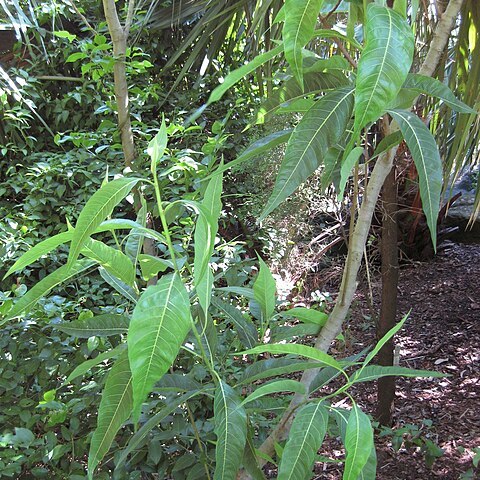
A fig. It is a small to medium sized tree. It is 5-10 m high. The branches droop. The trees are separately male and female. The leaves are long and sword shaped. The leaves are coarse to rough on both surfaces. The blade is 12-25 cm long by 2-4.8 cm wide. They are light green above and paler underneath. The veins taper to the long pointed tip. The flowers are very small in a fleshy receptacle. The fruit is enclosed in a fig receptacle. These are 1-1.5 cm across. They occur singly or in pairs in the axils of leaves. The fruit is edible.