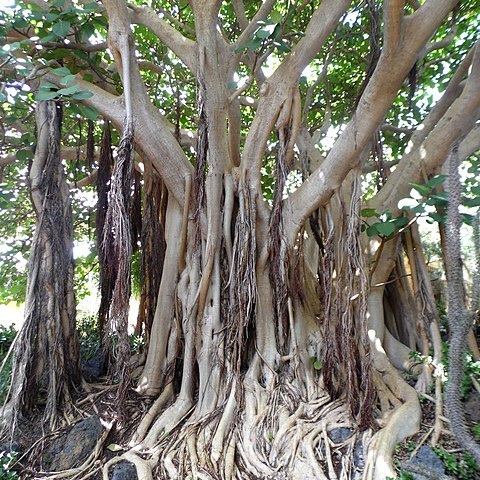
Tree up to 25 m. tall, (secondarily?) terrestrial.. Leafy twigs 6–15 mm. thick, yellowish to whitish or brownish hirsute to hirtellous, periderm flaking off when dry.. Leaves in spirals; lamina coriaceous, cordiform to ovate, subcircular or elliptic to subreniform, (5–)8–25(–35) × (2.5–)4–23(–25) cm., apex rounded to obtuse or very shortly and bluntly acuminate, base cordate, margin entire or almost so; upper surface rather sparsely hirtellous to puberulous or almost glabrous, lower surface whitish subvelutinous or densely to sparsely hirtellous, puberulous or almost glabrous; lateral veins 5–10 pairs, the basal pairs branched, reaching the margin usually at or above the middle of the lamina; tertiary venation for the greater part scalariform; petiole (1.5–)3–12(–19) cm. long, 1.5–4 mm. thick, periderm flaking off when dry; stipules 2–5 cm. long, on flush up to 8.5 cm., whitish to yellowish or brownish subhirsute to subsericeous, caducous.. Figs in pairs or solitary in the leaf-axils or just below the leaves, subsessile or on peduncles up to 6 mm. long; basal bracts 3.5–4.5 mm. long, free parts caducous.. Receptacle subglobose to ellipsoid, 2–2.5 cm. in diameter when fresh, 1–1.5 cm. when dry, whitish to yellowish velutinous or sparsely hirtellous, often ± verruculate, green with paler spots at maturity.
More
A fig. It is a tree. It grows up to 25 m tall. The crown is spreading and rounded. Sometimes the tree grows attached to other plants. The young branches are thick with soft dense hairs. They are 5-12 mm thick. They are yellow-brown. The leaves are stiff and almost round. They are 8-25 cm long by 4-23 cm wide. The tip is rounded but often with a blunt point. The leaf base is rounded and heart shaped. The leaf stalk is 3-12 cm long and hairy. The veins below the leaf are well marked. The veins fork near the edge of the leaf. The fruit are figs. One or 2 occur together near the leaves. They hardly have any stalk. They are almost round and 2 cm across. They are green with paler spots when ripe. The figs are hairy but have a clear opening.
A tropical plant. It grows in dry savannah near rivers. In East Africa it grows between 1,400-2,500 m altitude.
Plants grow naturally from seed. They can also be grown from cuttings. The figs have plenty of seed and these should be extracted from the figs and dried before planting. Seed can be stored for 2 months. Plants should be put at a wide spacing. The pollinating wasp is Elisabethiella socotrensis (Mayr.).