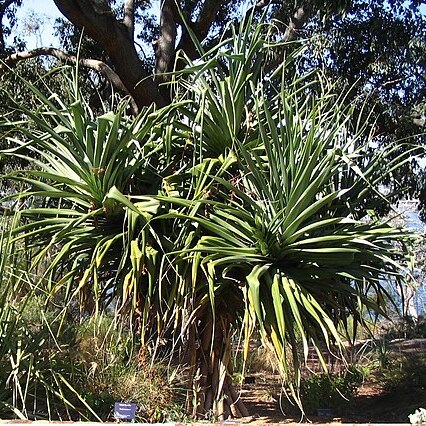
Tree to 6 m high, clump-forming; aerial or prop roots sometimes present; trunk with visible leaf-scars, smooth or with short ascending rootlets. Leaves erect to arching or drooping, to 1.4 m long, to 6 (–11) cm wide, not glaucous; margins with prickles from base, becoming smaller and finally absent at apex; midrib with prickles, absent towards apex. Male flowers: stemonophores to 12 mm long, with 4–11 stamens; anthers to 3 mm long. Fruiting head unbranched, pendent, globular, c. 15–18 cm diam., yellow to orange. Drupes usually solitary, free, very rarely connate in pairs, clavate, 25–44 × 5–9 (–11) mm, irregularly 4–6-angled in upper third, acute to rounded; stigma apical, sometimes ± oblique.