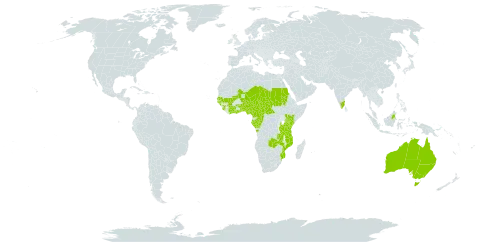
Particularly found on areas such as farm woodland which are subject to semi-permanent cultivation, also open woodlands on savannahs, rocky slopes, stony ridges etc.
| Life form | perennial |
| Growth form | tree |
| Growth support | free-standing |
| Foliage retention | deciduous |
| Sexuality | hermaphrodite |
| Pollination | entomogamy |
| Spread | - |
| Mature width (meter) | 1.0 |
| Mature height (meter) | 20.0 |
| Root system | tap-root |
| Rooting depth (meter) | - |
| Root diameter (meter) | - |
| Flower color | |
| Blooming months | - |
| Fruit color | - |
| Fruiting months | - |
| Nitrogen fixer | present |
| Photosynthetic pathway | c3 |
| Light |
|
| Soil humidity | |
| Soil texture | |
| Soil acidity | |
| Soil nutriment | - |
| Hardiness (USDA) |
| Uses | animal food bee plant coffee substitute drinks dye eating environmental use fiber fishing fodder food food additive forage fuel gene source invertebrate food material medicinal poison seasoning soap social use species spice tanning timber vertebrate poison wood |
| Edible | barks flowers fruits leaves pods roots seeds |
| Therapeutic use | Coffee (unspecified), Colic (unspecified), Fever (unspecified), Spice (unspecified), Toothache (unspecified) |
| Human toxicity | - |
| Animal toxicity | - |
| Mode | cuttings seedlings |
| Germination duration (days) | - |
| Germination temperacture (C°) | - |
| Germination luminosity | - |
| Germination treatment | soaking |
| Minimum temperature (C°) | - |
| Optimum temperature (C°) | 28 - 40 |
| Size | - |
| Vigor | - |
| Productivity | - |

| LSID | urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:941491-1 |
| WFO ID | wfo-0000179230 |
| COL ID | 4DN4B |
| BDTFX ID | - |
| INPN ID | 969136 |
| Wikipedia (EN) | Link |
| Wikipedia (FR) | Link |