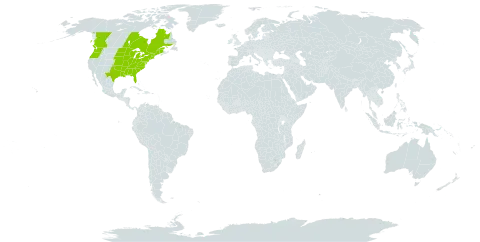
Erect, 2–7 dm, simple or branched above, glabrous below, stipitate-glandular in the infl; lvs lanceolate to narrowly elliptic, 5–10 cm, sharply serrate, acuminate at both ends; cymes 2–8 cm; sep oblong-lanceolate; capsule 5–6 mm wide; 2n=18. Marshes and muddy soil; Me. to Ont. and Minn., s. to Fla. and Tex. July–Sept.
A herb. It is fleshy and has underground runners. It grows 1 m tall. The leaves are alternate and they have short leaf stalks. The flowers are small with many together at the ends of the branches.