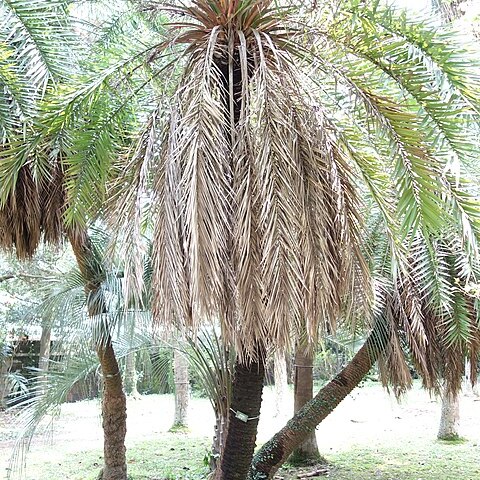
Stems solitary or clustered, 1-6 m tall, 20-40 cm in diam., sometimes short and subterranean, rough with persistent, diamond-shaped leaf bases. Leaves to 2 m; sheath and petiole to 40 cm; rachis 1-2 m; acanthophylls ca. 15 per side of rachis; pinnae 40-130 per side of rachis, linear, irregularly arranged and spreading in different planes; middle pinnae 20-50 × 1-4 cm. Male inflorescences erect, to 65 cm, with to 30 rachillae, these ca. 10 cm; female inflorescences erect, becoming arched, to 2 m, with to 40 rachillae, these to 40 cm. Fruits black, blue-black, or dark purple, ovoid to obovoid, to 1.8 × 0.9 cm; endosperm homogeneous.