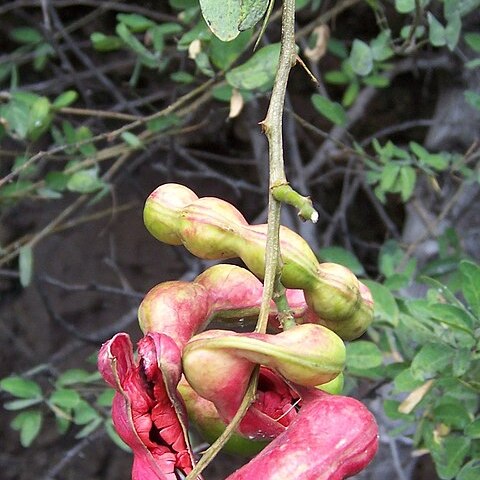
Trees or shrubs, often armed with spinescent stipules. Leaves bipinnate; petiole normally with a gland at its apex at the junction of the pinnae; pinnae usually with 1–3 pairs of leaflets, rarely more. Inflorescences of heads or spikes often racemosely or paniculately aggregated. Flowers usually hermaphrodite, usually sessile. Calyx gamosepalous with (4–)5(–6) teeth. Corolla (4–)5(–6)-lobed, puberulous to glabrous outside. Stamens many, fertile, their filaments connate below into a tube; anthers eglandular at apex. Ovary usually puberulous. Pods compressed or convex, spirally twisted, circinate or curved, splitting into 2 twisting coriaceous or subcoriaceous valves. Seeds unwinged, without endosperm, often arillate.
Trees or shrubs armed by spinescent stipules and stipella. Leaves bipinnate, not sensitive to the touch; rachis and pinnae usually with extrafloral nectaries. Inflorescences composed of pedunculate glomerules or corymbs which are aggregated into terminal or axillary panicles. Flowers uniform, bisexual, pentamerous. Calyx connate, valvate. Corolla connate, valvate. Stamens numerous, united in a tube at the base. Ovary solitary. Pods straight or spirally contorted, flat, dehiscing along both sutures, in most species dark brown outside, reddish orange within. Funicle in most species developed into an aril, covering the proximal part of the seed. Seeds brown or blackish, wingless, obovate or asymmetric, with areole.
Trees [or shrubs], armed by spinescent stipules and stipels. Leaves bipinnate, not sensitive to touch; rachis and pinnae usually with extra-floral nectaries; leaflets 1 [to several] pairs per pinna. Inflorescences pedunculate heads or corymbs aggregated in terminal or axillary panicles. Flowers uniform, bisexual, 5-merous. Calyx shortly toothed. Corolla gamopetalous, 5-lobed. Stamens numerous, united into a tube at base. Ovary solitary. Legume spirally contorted [or straight], in most species dark brown outside, reddish orange within, flat, dehiscing along both sutures. Seeds brown or blackish, obovoid or asymmetric; testa hard, with a pleurogram; funicle developed into an aril.