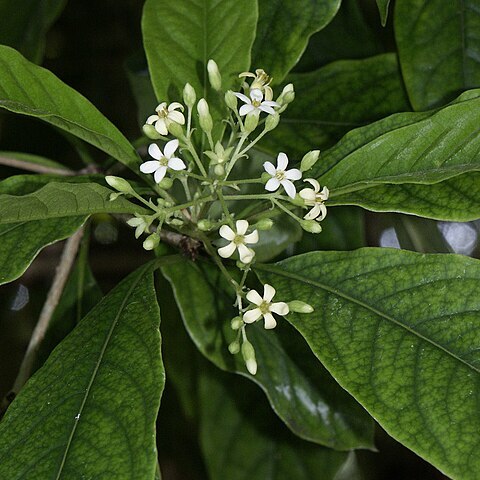
Small, rounded, dioecious tree to 7 m high; bark smooth, white; sparse white indumentum of short base, short-arm white T-shaped hairs on new shoots and peduncles. Cotyledons two, c. 20 mm x 8 mm ovate, almost sessile. Seedling leaves immediately alternate, broad ovate, bright glossy dark green with yellow venation, lower surface paler. Adult leaves whorled; lamina elliptic to obovate, 110–135 mm long, 40–45 mm wide, attenuate; margins undulate; apices rounded, slightly emarginate; glossy green-yellow with raised 8–12 secondary veins not prominent; petiole 20–30 mm long. Inflorescences exserted terminal, aggregated branched umbels of unisexual flowers with parts in fives regularly placed around the pistil; main rachis stout, to 38 mm long; individual pedicels short, 8–10 mm long; involucre caducous. Sepals tiny, cupular with only the ends of the lobes free, rounded. Petals briefly connivent at the base only, 6–8 mm, white, linear to spathulate, apices recurved. Male flowers: anthers prominent, exserted to 2 mm long, ovoid with a prominent mucro, golden yellow dehiscing gold pollen; filaments 3 mm long only, slightly adnate to petal joins in bud. Pistil with barely distinguished stipitate ovary, merging into the style, terminating in a slightly knobby stigma; ovary with few or no ovules; sparsely hairy only. Female flowers: with shrivelled anthers not exserted past the stigma and without pollen. Pistil to 5 mm long, from the distinct basal nectary to the fat, capitate stigma; style short, distinct; ovary globular-obovate, densely hairy towards the base, almost completely bilocular with the placentas meeting at the septum but not fusing (Northern Territory), or appearing unilocular without raised placentas (Western Australia), with numerous ovules inserted in two rows in each loculus. Considerable variation exists within and between these these two sex forms in Australian stands. Fruits are loculicidally dehiscent capsules, 12–20 mm long, thick, woody, globular, orange-brown, inner bright yellow with a red placenta, valves strongly recurved; seeds numerous 2–4 mm long, chunky, glossy black, cohering.
More
Shrub or tree, (2-)8-l5(-20) m high; young shoots often ferrugineous-pubescent. Leaves spirally arranged or crowded towards the ends of the twigs, subcoriaceous, very variable in shape and size, generally narrowly elliptic, narrowly obovate or oblanceolate, rarely narrowly ovate, c. 5-15(-23) by 2½-5½(-7) cm; base cuneate, generally decurrent, margins generally undulate, top gradually or abruptly shortly acuminate, often also rounded; nerves c. 6-12 pairs, reticulations fine; petiole c. 1-2 cm. Inflorescences terminal or axillary subsessile or peduncled fascicles or panicles, peduncles up to c. 6 cm. Bracts linear, acute, pubescent, c. 3 mm long. Pedicels c. 1-6 mm. Sepals nearly free or united to varying degree, narrowly elliptic or lanceolate, sometimes the calyx split to the base at one side, c. 4 mm long, tops acute or rounded. Petals ligulate, (9-)10-12(-15) by 2 mm. Stamens in ♂ flowers c. 8-12 mm, in female flowers c. 4.5-6 mm; anthers in ♂ flowers oblong, c. 1½-3 mm, apiculate, in female flowers triangular or sagittiform, c. 0.5-1.5 mm. Ovary stipitate or almost sessile, in ♂ flowers c. 5 by 1 mm, in female flowers ellipsoid, c. 3-5 by 1.5-2 mm, glabrous or pubescent (the base, the lower half, or entirely); style in ♂ flowers c. 4 mm, in ♀ flowers c. 2 mm; stigma in ♂ flowers not, in ♀ flowers distinctly thickened. Fruits solitary or few, ellipsoid, compressed-obovoid or-globose, mucronate, c. (1-)2-4(-5) by (1-)1½-2(-3) cm, 2-valved; valves thick-fleshy, in the median line c. 3-6 mm thick, recurving when dry, margins readily incurved when dry, undulate, rugose; funicles inserted up to near the top. Seeds many, of variable size.
In light, rather dry woods, mixed mon-soon-forest, tjemara forest, steep and bare slopes, occasionally near the sandy beach, on rocky shores, on sand, limestone or volcanic soil, in Java generally between 1000 and 2000 m, in the Philippines between 600 and 1500 m, but here as well as elsewhere also often at lower altitude.