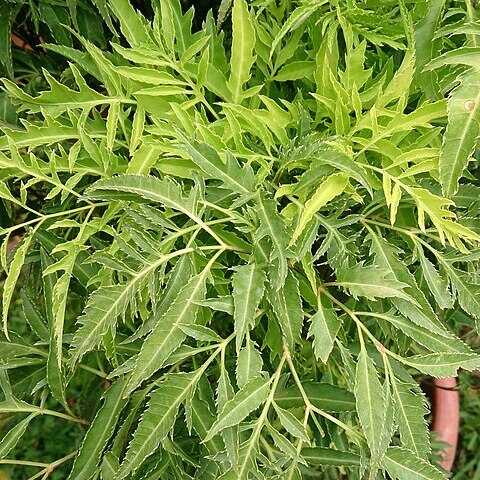
Shrubs or treelets, 1.5-4 m tall, andromonoecious. Leaves 1-or 2-pinnate; petiole 8-20 cm, clasping at base, alate for 3-4.5 cm with membranous wings; petiolules 0.5-3 cm; leaflets 9-15, often variegated, elliptic to lanceolate or ovate, often narrowly so, 10-35 × 2-10 cm, papery, base obtuse to attenuate, margin entire to coarsely crenate, often with minute teeth, apex acuminate or acute to obtuse. Inflorescence terminal, pendent, a panicle of umbels; primary axis 15-30 cm; secondary axes 5-7, usually in verticils, 20-80(-140) cm; tertiary axes 10-25 per secondary axis, mostly grouped in 2-4(or 5) verticils, with a terminal umbellule of bisexual flowers and 2-6 lateral umbellules of staminate flowers, or further divided into 4th order axes; pedicels 4-8 mm (shorter in staminate flowers). Ovary (2 or)3-5-carpellate; styles free nearly to base, 1-1.4 mm at anthesis, diverging, expanding in fruit to 1.7 mm. Fruit subglobose to broadly ovoid, 3-4(-5) mm high, base often shallowly cordate. Fl. autumn.
A shrub or small tree. It grows 2-5 m high. The leaves are alternate and they are divided into leaflets along the stalk. The leaves are 50-100 cm long by 6-12 cm wide. There is a sheath base. The leaflet shapes can vary even on the one plant. The flowers are in a large branched group at the end of the stalk.