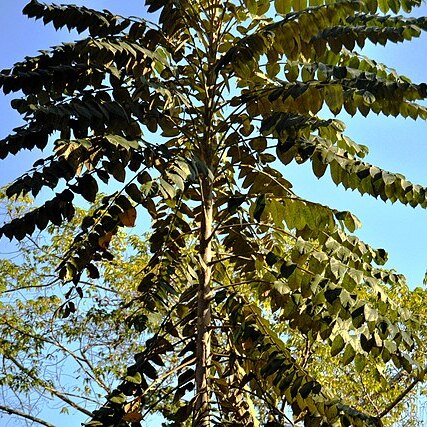
Leaflets (3)6–7(12)—paired, up to 12(17) × 5(7·5) cm., sessile or with petioles of up to c. 10 mm. long, coriaceous (often strongly so), lanceolate-ovate (the terminal leaflet often broader and more ovate than the lateral paired ones); apices acute, often with a small mucro, rarely obtuse and emarginate; bases rounded to subcordate (rarely subcuneate); margins entire to slightly undulate, more or less convolute, becoming leathery and subglabrous, the lower surface more or less densely tomentose.
Primary axes up to 40(70) cm. long, tomentose to subglabrous, bearing numerous laterals of 8(12) cm. long, densely crowded with flowers, but elongating somewhat as the fruit matures.
A tall tree up to 30 m. high with a long unbranched trunk, eventually dividing into primary and secondary branches in a very regular manner.
Leaves up to 80 cm. long, regularly pinnate, usually imparipinnate though examples lacking the terminal leaflet are encountered.
The large leaves bunched at the top of the rather few branches; leaflets white-tomentose beneath, dark green above
Fruit broadly-ovoid to subglobose, 3–4(6) × 3–5 mm., glabrous to slightly pubescent, somewhat ribbed.
Pedicels up to 5 mm. long; petals greenish to creamy white, flowers honey-scented.
Stylopodium somewhat depressed, styles widely divergent for most of their length.
Inflorescence a complex of compound racemosely arranged racemes.
A tree, 20–50 ft. high, rarely to 100 ft.
Flowers cream