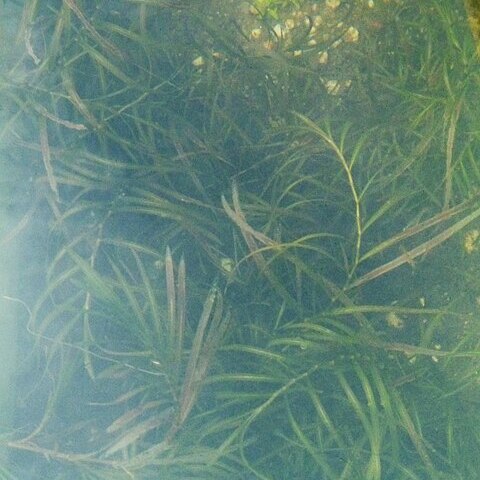
Vertical shoot aseasonal, continuously growing, without specialised winter buds; stem filiform, terete, much branched, horizontal shoots not much differentiated, much branched. Floating leaves absent; submerged leaves linear, slightly falcate, sessile, lamina 50-120 by 2-3.5 mm, 5-7(-9)-veined, with 2-16 inconspicuous sclerenchymatous strands, apex acuminate, margin entire; stipules axillary, convolute, 15-25 mm, obtuse. Spikes cylindrical, contiguous, 10-15 mm; peduncles 20-40 cm. Flowers 5-9, with 4 carpels. Fruits broadly elliptic-ovate, 3.2-3.8 mm, rarely developed, beak short. Stem anatomy: Stele of oblong type. Endodermis of O-type. Interlacunar bundles absent, subepidermal bundles present. Pseudohypodermis absent. Chromosome number: 2n = 26.
A plant that grows in water. The stems are slender and have many branches. The stipules form sheaths. The leaf blades are narrow and 5-10 cm long by 2-3 mm wide. They taper at the tip. The flowers are very small and in spikes in the axils of leaves.