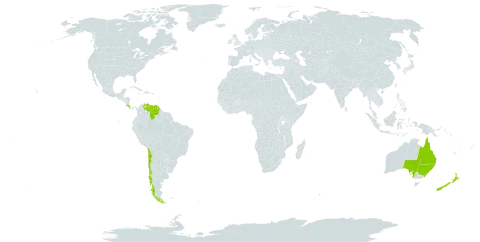
Dioecious trees or shrubs. Seedling and adult leaves large (more than 5 cm long), bifacially flattened, with a distinct midrib, hypostomatic, linear to oblong, spirally arranged; secondary transfusion tissue present; hypodermis absent; a single resin duct present below the vascular bundle. Male cones terminal on short axillary shoots, comprising numerous spirally arranged sporophylls. Female cones 1-several on short, scaly axillary shoots or peduncles, reduced to a single fertile scale with 1 inverted ovule; receptacle small, not enlarging at maturity; peduncle with numerous scaly bracts. Seeds not beaked.
Dioecious trees or shrubs. Seedling and adult leaves small (less than 2.5 cm long), bifacially flattened, with a distinct midrib, hypostomatic, linear to oblong, spirally arranged; secondary transfusion tissue absent; hypodermis present; a single resin duct present below the vascular bundle. Male cones terminal on short axillary shoots, comprising numerous spirally arranged sporophylls. Female cones 1-several on short axillary shoots or peduncles, reduced to a single fertile scale with 1 inverted ovule; receptacle small, not enlarging at maturity; peduncle with numerous scaly bracts. Seeds not beaked.