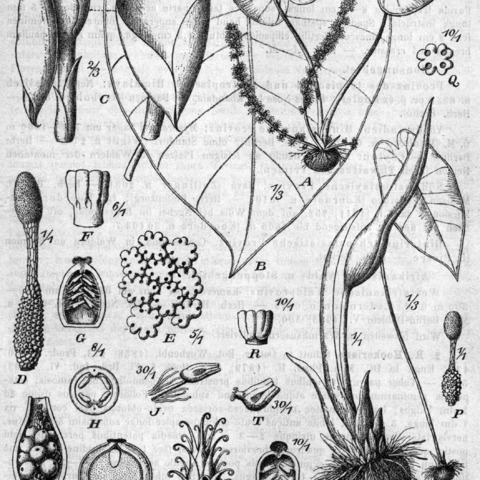
Tuber depressed globose, 2-4 × 3.5-5 cm; stolons erect, simple, stout; bulbils ellipsoid, 0.5-2.5 mm, stout; bristles to 1.5 mm, stout. Cataphylls 4 or more, brownish, broad, concealing peduncle, ca. 15 × 3 cm. Petiole 19-42 cm, proximal 1/4 sheathing; leaf blade glossy on both sides, pale green abaxially, green adaxially, oblong-ovate or lanceolate, 11-33 × 7-19.5 cm, sinus 1.5-3 cm; intramarginal vein indistinct. Flowering before leaves develop. Peduncle 6-12 cm. Spathe tube green outside, 3-5 × 1.3-2 cm; limb initially erect, later reflexed, yellow inside, obovate, 5.3-11.5 × 2.5-9 cm, narrowed to base, apex acute, apiculate. Spadix: female zone 1.7-2 cm × 7-9 mm, with 3 or 4 whorls of sterile ovaries at apex and 1 or 2 whorls at base; sterile zone 1.1-2.5 cm, slender, tapering distally; male zone yellowish, clavate, cylindric, 1.5-2.2 cm × 4-7 mm. Fl. Apr-Sep. 2n = 28, 42.
Lithophytic herb; corm subhemispherical, to c. 5 cm diam.; stolons erect, unbranched, to c. 30 cm long, bearing numerous clusters of ovoid hooked bulbils. Leaves 1–several together; petiole to c. 50 cm long, sheathing in lower c. ¼; blade broadly ovatosagittate, peltate, shining bright green, ±pendent, to c. 40 cm long; secondary venation not forming interprimary collective veins. Inflorescence seldom found (in Australia), mostly solitary or 2 together in series, produced before leaves; spathe c. 11 cm long, constricted; lower spathe narrowly ovoid, green; spathe limb broadly spathulate, yellow; spadix reaching c. 1/2 length of spathe limb; male zone clavate.
A herb which forms tubers. These are 2-4 cm across. It grows to about 30-50 cm high. It keeps growing from year to year. The leaves have long stalks. These can be 30-50 cm long. The leaves are simple and 21-40 cm long by 15-18 cm wide. The leaves are almost round and taper to the tip. The leaves can be purple underneath. The bract around the flower is pinkish. The flower is a spike. This is about 17 cm long.
Flowers appearing rarely and during leafless stage
Bulbiliferous shoot leafless and brown.
Spathe greenish cream coloured
Spadix whitish