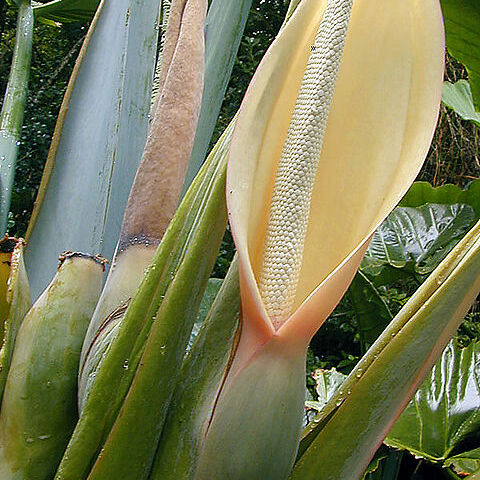
Herbs, perennial, terrestrial, epiphytic or aquatic, often with milky, viscid or acrid sap; stems lianescent, tuberous, rhizomatous or reduced. Leaves alternate, 1–many, petiolate, usually some reduced to scale leaves (cataphylls) before or among normal leaves or inflorescences; petiole typically with distinct basal sheath, often pulvinate at or near apex; lamina usually broad, membranous to coriaceous, very variable in size and shape, simple or variously lobed, sometimes perforated; main venation pinnate, palmate, pedate or rarely parallel, finer venation reticulate or striate. Inflorescence pedunculate, consisting of fleshy ± cylindric spadix (spike) subtended by bract-like spathe; spathe usually spreading above and convolute below, rarely with margins connate near base, often variously coloured; spadix either uniform with bisexual flowers or monoecious with pistillate flowers at base, staminate flowers above, sterile flowers of varying shape often present at base, middle or apex, apical portion sometimes forming a sterile appendix. Flowers numerous, minute, sessile, bractless, naked or perigoniate, bisexual or unisexual; perigon (perianth) cup-like or composed of 4–9 free or ± connate tepals. Stamens opposite tepals, free or connate into synandria; anthers sessile or with elongated filaments, opening by lateral or apical slits or pores; connective often very thick. Ovary normally superior, 1–many-locular; locules each with 1–many ovules; placentas parietal, axile, basal or apical; stigma sessile or borne on short, conical, rarely attenuate style. Fruit a 1–many-seeded berry, rarely connate to form a syncarp, often brightly coloured. Seeds minute to large, variable in shape, with or without endosperm
Herbs, perennial, wetland or terrestrial, occasionally emergent or floating, [often epiphytic or climbing], usually with milky or watery latex, rarely colored. Rhizomes, corms, or stolons present; rhizomes vertical or horizontal, creeping at or near surface, sometimes branched; corms underground, starchy; stolons at or near surface. Stems absent [sometimes aboveground or aerial]. Cataphylls usually present. Leaves rarely solitary, alternate or clustered; petiole rarely absent, with sheathing base; blade simple or compound [occasionally perforate], elliptic to obovate or spatulate, occasionally sagittate-cordate, larger than 1.5 cm; venation parallel or pinnate-or palmate-netted. Inflorescences spadices, each with 3--900 usually tightly grouped, sessile flowers, subtended by spathe; spathe rarely absent, persistent (sometimes only proximally) or deciduous, variously colored; spadix cylindric or ovoid, various parts occasionally naked or with sterile flowers. Flowers bisexual or unisexual, staminate and pistillate usually on same plants or functionally on different plants, staminate flowers distal to pistillate when unisexual; perianth absent or present; stamens 2--12, distinct or connate in synandria; ovaryies 1, 1--3(--many)-locular, sessile or embedded in spadix; styles 1; stigmas hemispheric, capitate, or discoid [sometimes strongly lobed]. Fruits berries, distinct or connate at maturity. Seeds 1--40(--many) per berry.
Massive to slender climbers or hemi-epiphytes, arborescent to geophytic and rhizomatous to cormous, terrestrial, lithophytic or aquatic herbs. Leaves alternate, distichous or spiral, evergreen to deciduous, petiolate to apetiolate (Gymnostachys), sheathing, sometimes geniculate, highly compound to linear, with reticulate to striate venation. Inflorescences solitary to multiple and sympodially clustered, a spadix subtended by a ± conspicuous sometimes constricted spathe (absent in Gymnostachys), often thermogenic, sometimes foul-smelling. Flowers bisexual throughout spadix or unisexual, tepalate or atepalate, with number of parts varying; monoecious spadices with female zone lowermost, then male zone sometimes separated from female by sterile interstice of variously shaped neuter organs or naked, with distal portion of spadix a sterile appendix, or this absent. Stamens with differentiated anther and filament or truncate and then sometimes connate into synandria; anthers dehiscing through longitudinal slits or apical pores. Ovary superior or naked, plurilocular to unilocular (pseudomonomerous); placentas axile to basal or parietal; stigmas slit-like to punctate to lobed, sessile or not. Fruit mostly a berry, sometimes protected until ripe by spathe, rarely fleshy dehiscent. Seeds with or without endosperm; testa membranous to thickened.
Aquatic plants floating free on or in water, reduced to small glabrous leaf-like or globular fronds. Fronds single or 2–many, cohering together at their bases, 0.5–15 mm long (without stalk), 0.3–10 mm wide, thin or thick; new fronds (daughter fronds) arising successively in 1 or 2 pouches or in cavity at base of mother frond. Turions present in some species. Roots absent or 1–21 (without root hairs). Flowers (interpreted as an inflorescence by many authors) rare in many species, 1 or 2 per frond; sepals and petals none; stamens 1 or 2; ovary 1, bottle-shaped, tapering into short style; stigma funnel-shaped. Fruit with dry pericarp, 1–5-seeded.
Leaves solitary or few, sometimes appearing after the flowers, mostly radical, when cauline then alternate and distichous or spirally arranged, entire or variously divided, often hastate or sagittate, with a membranous sheath at the base
Flowers small, arranged on a spadix enclosed in a spathe, bisexual or monoecious, the males in the upper part, females below, rarely dioecious
Stamens hypogynous, 2-4-8, opposite the perianth-segments; anthers opening by pores or slits, free or united
Herbs with watery, bitter or milky juice, with a tuberous or elongated rhizome, rarely woody and climbing
Perianth present in the bisexual flowers or absent from the unisexual flowers
Ovary superior or immersed, 1-many-locular; style various or absent
Fruit a berry, or coriaceous and rupturing, 1-many-seeded
Ovules parietal, axile, basal or apical
Seeds mostly with copious endosperm