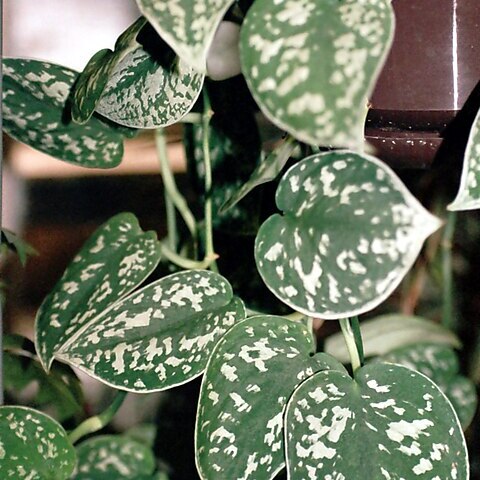
Lianas, creeping and climbing against trees with aid of adhesive roots. Stem robust, branched. Leaves spiro-distichous; petiole usually sheathing or winged throughout its length; leaf blade undivided, pinnately veined, with very numerous parallel, thin lateral veins. Inflorescences solitary, near stem apices; peduncle at last laterally protruding from petiolar sheath. Spathe not constricted, initially involute and tubular, afterward somewhat inflated, finally expanding only by a rather narrow longitudinal slit, never entirely or conspicuously flat-spreading, falling off as a whole leaving a thick scar on apex of peduncle. Spadix drying black, cylindric, much thicker than peduncle. Flowers many, bisexual, naked. Stamens 4; filaments strap-shaped. Ovary with flat, often subrhomboid or quadrangular apex, 4-6-angular, 1-loculed; ovule 1, basal; stigma sessile, disciform to linear. Seeds subreniform.