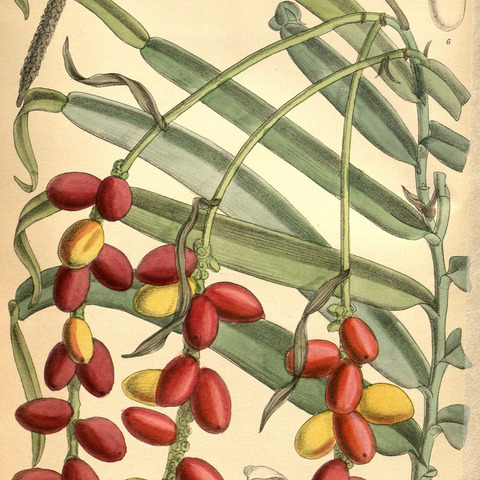
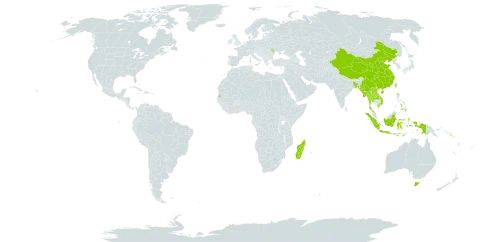
Rather to very slender usually hemi-epiphytic root climbers, usually with rather clearly differentiated adherent, non-flowering and free, flowering shoots, the latter of which may be highly ramified; flagelliform foraging shoots with reduced leaves often produced; juveniles sometimes heteroblastic (not known in Australia). Leaves distichous; petiole either with a narrow, ±clasping membranous sheath and a conspicuous apical geniculum (subg. Allopothos) or broad, flattened and lamina-like, with a small apical articulation (subg. Pothos); blades entire, ovate to elliptic, with reticulate venation; primary lateral veins fine, crossed on each side of midrib by 1 or more intramarginal veins. Inflorescences solitary to few in series and terminal on leafy shoots to axillary and then subtended by a series of cataphylls, or borne on specialised perennial foliage-leafless flowering branch systems (not in Australia); spadix sessile to stipitate, compact to very lax-flowered (not in Australia); spathe mostly inconspicuous, bract-like, usually reflexed, white to green to purple-brown. Flowers bisexual, with a perianth of 6 (rarely 4) free (rarely united) tepals. Stamens 6 (rarely 4), free, with flattened filaments. Ovary trilocular; locules uniovulate; stigma punctate. Fruit a 1–3-seeded berry, large relative to spadix.