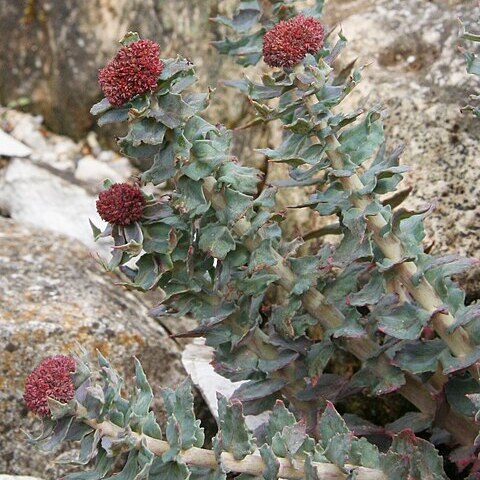
Herbs, perennial (dying back in winter to rootstock), not viviparous, 0.3-6 dm, glabrous [pubescent]. Stems a rootstock with apex mostly above ground, erect, spreading, or decumbent, commonly branching to form clumps, fleshy, with brown scalelike [or green] leaves; flowering stems from axils of brown scale-leaves on stout rootstock partly above ground. Leaves persistent, cauline, alternate, sessile, subclasping basally; blade elliptic to ovate or oblanceolate to linear, obovate, or oblong, laminar (mostly to 1 mm thick), 0.5-5.5 cm, somewhat fleshy, base not spurred, margins entire or toothed; veins not conspicuous. Inflorescences cymose or spikelike to subcapitate. Flowers bisexual or unisexual, erect, 4-6-merous; sepals connate basally, all alike (unequal in R. rosea); petals erect or spreading, distinct, greenish, white, rose, dark red, or yellowish; calyx and corolla not circumscissile in fruit; nectaries quadrate to linear; stamens 2 times as many as sepals, epipetalous; filaments mostly adnate to corolla at base; pistils erect, nearly distinct; ovary base straight; styles 2+ times shorter than ovary. Fruits erect. Seeds oblanceoloid or pyriform, ribbed, finely cross-ribbed.