Herbs, annual, terrestrial or amphibious, to ca. 40 cm. Stem creeping and branched at base, ascending, or erect, terete to weakly 4-angled. Leaves decussate, obovate-elliptic or obovate-oblong, 5-17 × 3-8 mm, base cuneate, margin translucent to opaque, white cartilaginous, apex obtuse. Bracts like foliage leaves or distinctly smaller on axillary spikes. Flowers in axillary spikes or sessile in bracts on main stem; bracteoles linear, reaching sepals or longer. Floral tube 4-merous, pink-red at anthesis, narrowly to broadly campanulate, 1.5-2.5 mm, 4-angled; sepals 4, lanceolate-deltate; epicalyx absent. Petals 4, pink, minute to ca. 1/2 as long as sepals. Stamens 4; anthers reaching sinus of sepals. Ovary ellipsoidal; style ca. 1/2 as long as ovary, slightly exserted. Capsule ellipsoidal, ca. 1 mm in diam., slightly exserted, 2-valved. Seeds ca. 0.4 mm. Fl. Sep-Oct, fr. Oct-Apr. 2n = 32*.
More
An annual herb. It can grow on land or in water. It is about 40 cm high. The stems are creeping and branched at the base. It can be weakly 4 angled. The leaves are divided and broadly oval. They are 5-17 mm long by 3-8 mm wide. The flowers are small and 1-2 mm long. They are in spikes 6-12 mm long in the axils of leaves. The fruit is an oblong capsule 1.5 mm long. It has lines along it. The seeds do not have wings.
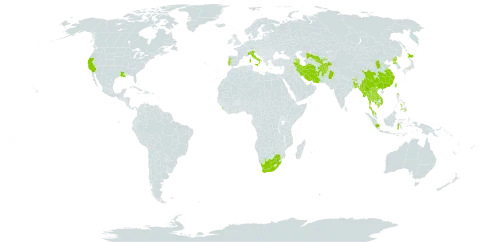
It grows in temperate and tropical places. It is common in central and southern China. It is usually associated with rice cultivation. It grows in wetlands. In Pakistan it grows between 300-1,800 m altitude.