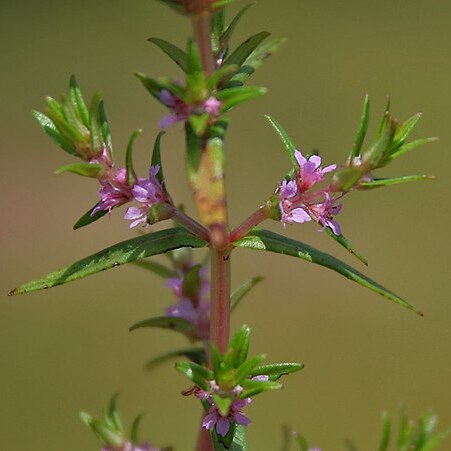
Herbs, annual or perennial, aquatic, amphibious, or terrestrial, often anthocyanic with age. Stems glabrous, simple or branched, commonly 4-angled or 4-winged. Leaves decussate or whorled, sessile or subsessile; bracts of inflorescences like foliage leaves or smaller and different in shape. Flowers actinomorphic, monomorphic [or dimorphic], (3 or)4(-6)-merous, solitary, sessile or shortly pedicellate, in axils of bracts on main stem, on spikelike lateral branchlets, or in terminal spikes. Floral tube campanulate or urceolate, generally globose in fruit; bracteoles 2, at base of floral tube; sepals 3-6, ca. 1/3 length of floral tube or less, deltate; epicalyx alternating with sepals or absent. Petals 3-6, pink-purple to whitish. Stamens 1-6, opposite the sepals. Ovary 2-4-loculed; style long or short; stigma capitate, rarely more massive, discoid. Capsule finely transversely striate (10 × magnification), hyaline, septicidally dehiscent, 2-4-valved. Seeds numerous, brown or reddish brown, ovoid to ellipsoidal, concave-convex, less than 1 mm.
Aquatic or palustrine herbs, glabrous throughout, simple or sparsely branched. Leaves opposite or verticillate, sessile. Inflorescence of 1-flowered axillary cymes. Flowers usually 3-or 4-merous, bisexual, actinomorphic. Hypanthium appendic-ulate or exappendiculate, generally urceolate, membranaceous, the calyx lobes generally equal, valvate. Petals as many as the calyx lobes or absent. Stamens as many as the calyx lobes or fewer, equal, included, the anthers ovoid or oblong-ovoid, the filaments inserted about one-third from the base of the hypanthium. Ovary 3-or 4-carpellary, sessile or with a short gynophore, 1-locular, the placentation free-central; ovules many; stigma capitate. Fruit a horizontally striate septicidal capsule; style and hypanthium persistent; seeds minute.
Annual or perennial glabrous herbs. Stems creeping, ascending, erect or floating, simple or branched. Leaves decussate or whorled, sessile or rarely shortly petiolate; stipules absent. Flowers solitary in axils of bracts, usually regular, 3–5-merous. Hypanthium usually campanulate, sometimes semi-globose or sub-urceolate; appendages 3–5 or absent. Petals 3–5 or absent. Stamens 2–5, never more than sepals. Ovary 2–4-locular. Capsule dehiscing septicidally by valves; 1 valve crowned with persistent style.
Fls (3)4(–6)-merous; hypanthium campanulate to globose or urceolate, with (as in our sp.) or without intersepalar appendages; pet present or absent; stamens 4(–6); ovary imperfectly (3)4(–6)-locular; disk wanting; capsule septicidal, (2)3–4-valved, transversely minutely and densely striate; glabrous annuals of wet places, with small, inconspicuous, bibracteolate fls solitary in the axils. 45, mainly Old World tropics.
Calyx-tube semiglobose, campanulate or urceolate-tubular, scarious, very rarely herbaceous, the lobes triangular, alternating with ± developed appendages or these often absent; nectariferous ring present at base.
Flowers small, actinomorphic, homostylous or heterostylous, 3–6-merous, axillary, solitary, or in terminal racemes or spikes, very rarely in axillary umbels; bracteoles 2, rarely absent.
Ovary sessile or substipitate, incompletely 2–4-locular (dissepiments interrupted above the placentas); ovules ± numerous, small; style absent or ± developed, simple.
Capsule septicidally 2–4-valved, cartilaginous, the walls horizontally striate (under the microscope).
Leaves decussate or verticillate, rarely alternate, sessile or subsessile.
Annual or rarely perennial glabrous herbs, aquatic or in marshy places.
Petals persistent, sometimes caducous or absent, equal or unequal.
Stems terete or 4-gonous, striate, often rooting at the nodes.
Stamens 1-6, opposite to the sepals.
Seeds small, concave-convex.