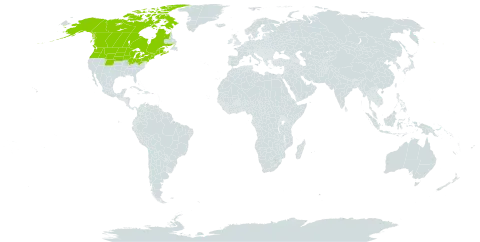
A trailing plant. The leaves are alternate and compound. There are 3 or 5 oval leaflets. They have sharp teeth. They are green on both sides. The flowers are white or pinkish. They are 12 mm across. They occur as several in small clusters. The fruit is a round berry.