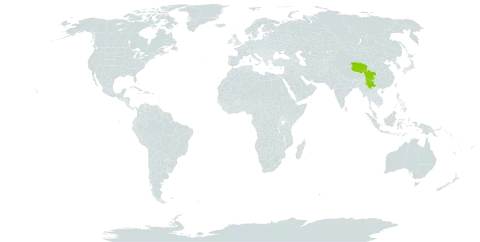
Shrubs 1–2 m tall. Branchlets brownish to dark brown, sometimes blackish, pubescent, with intermixed glandular hairs and prickles; flower bearing branchlets lateral, 5–8 cm, pubescent, with intermixed glandular hairs. Leaves imparipinnate, 3-foliolate; petiole 2–3.5 cm, petiolule of lateral leaflet 0.5–1.5(–2) cm, lateral leaflets subsessile, pubescent, with intermixed glandular hairs, with sparse, minute prickles; stipules linear, 0.6–1 cm, pubescent, with glandular hairs; blade of leaflets broadly ovate to narrowly ovate, rarely suborbicular, 2–4 × 1.8–3 cm, terminal leaflet slightly longer than lateral leaflets, both surfaces appressed pubescent, more densely so and with glandular hairs along veins abaxially, base rounded, usually subtruncate on terminal leaflet, margin with sparse, glandular hairs and irregularly minute sharply serrate, sometimes 3-lobed on terminal leaflet, apex obtuse or acute. Inflorescences terminal on lateral branchlets, corymbose, 2–4 cm, 3-or 4-flowered or more, or flowers solitary in leaf axils; rachis and pedicels with soft hairs, intermixed glandular hairs, and sparse, minute prickles; bracts linear, 4–7 mm, pubescent, with stalked glands. Pedicel (1–)1.5–3 cm. Flowers 1–1.5 cm in diam. Calyx purplish red, abaxially densely pubescent, with stalked glands, unarmed or with needle-like prickles; tube pelviform; sepals erect, lanceolate, 0.8–1.4 cm × 2.5–5 mm, apex acuminate. Petals white, tinged purplish, or purplish red, broadly elliptic or oblong, 5–6 mm in diam., slightly shorter than sepals, base shortly and broadly clawed, margin entire or sometimes erose. Stamens many, shorter than petals; filaments linear, basally broadened and flattened. Pistils somewhat shorter than stamens; ovary sparsely pubescent, glabrescent; styles glabrous. Aggregate fruit orange-red, subglobose, 8–11 mm in diam., glabrous; pyrenes somewhat reniform, alveolate. Fl. May–Jun, fr. Jul–Aug.
More
A shrub. It grows 1-2 m tall. There are prickles. The leaves have leaflets along the stalks and one at the end. There are 3 leaflets. There can be 3 or 4 flowers at the ends of branches or single flowers in the axils of leaves. The flowers petals are white. The fruit is aggregate and orange-red. They are about 1 cm across. There are some botanical varieties.
Can be grown by cuttings or seedlings. Seeds needs stratification.