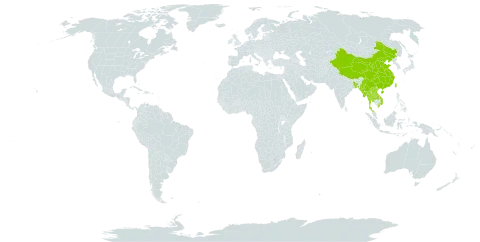
A climbing vine. It does not have prickles. The stem is branched. It is 1-4 m long and woody. The leaf stalk is 5-15 cm long and narrowly winged. There are tendrils. The leaf blade is oval or sword shaped and 6-15 cm long by 1-7 cm wide. The flowering stalk has 10-30 or more flowers. They are greenish white. The fruit is a round, blue-black berry. It is 6-10 mm across.