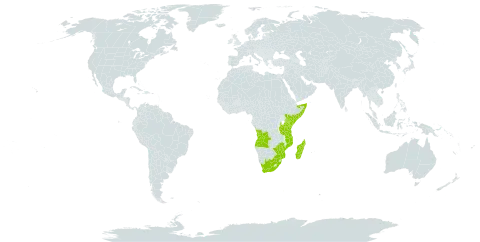
A glabrous shrub or small tree up to 10 m tall, rarely taller, generally dioecious; branches horizontal. Bark smooth, grey, often with fine longitudinal markings. Twigs greenish. Stipules 1 x 1 mm, triangular-ovate, subacute. Petioles 3-7 mm long. Leaf blades 2-13 x 1.5-7 cm, obovate to elliptic-oblanceolate, abruptly acutely acuminate at the apex, cuneate or ± rounded at the base, entire or sharply denticulate, coriaceous, glossy, paler beneath than above, often drying bright green or yellowish-green; lateral nerves in 5-9 pairs, looped; tertiary and quaternary nerves reticulate with raised pustules in the centre of each reticulation. Male flowers: pedicels 1-2 mm long; sepals 5, 2.5-3 x 2-2.5 mm, suborbicular, each with a yellow gland on the abaxial face, ciliate, the outer greenish, the inner creamy-white; glands confluent; stamens (6)14, usually in an outer whorl of 9 and an inner of 5, filaments 1-2 mm long, anthers 0.5-0.7 mm long. Female flowers: pedicels somewhat stouter than in the male flowers; sepals ± as in the male flowers; disk 5-angular or shallowly 10-lobed; staminodes small, subulate or occasionally staminiform; ovary c. 1.5 mm in diameter, 3-celled, subglobose, smooth; styles 3, 1 mm long, bifid, stigmas subulate. Fruit 7 x 8 mm, (1)3-celled, 3-lobed to subglobose, smooth, green. Seeds c. 4 x 4 mm, broadly compressed-ovoid, foveolate; exotesta red, grey when dry, endotesta red or black.
A shrub or small tree. It grows up to 4.5 m tall. The leaves are oblong and leathery. The tip has a blunt point and they narrow to the base. They are about 4-9 cm long and 2.5-5 cm wide. There are widely spaced teeth on the edge of the leaf. The midrib is raised under the leaf and there are 4-6 pairs of veins that loop along the leaf edge. The upper surface of the leaf is dark green and the lower surface is lighter. The leaves are on short stalks. The flowers are small and cream coloured. They are in small clusters opposite the leaves. The fruit are small and round. They have 3 lobes. They are 7 mm across. The juice of the fruit is edible.
Leaf blades 2–13 × 1.5–7 cm, obovate to elliptic-oblanceolate, abruptly acutely acuminate at the apex, cuneate or ± rounded at the base, entire or sharply denticulate, coriaceous, glossy, paler beneath than above, often drying bright green or yellowish-green; lateral nerves in 5–9 pairs, looped; tertiary and quaternary nerves reticulate with raised pustules in the centre of each reticulation.
Male flowers: pedicels 1–2 mm long; sepals 5, 2.5–3 × 2–2.5 mm, suborbicular, each with a yellow gland on the abaxial face, ciliate, the outer greenish, the inner creamy-white; glands confluent; stamens (6)14, usually in an outer whorl of 9 and an inner of 5, filaments 1–2 mm long, anthers 0.5–0.7 mm long.
Female flowers: pedicels somewhat stouter than in the male flowers; sepals ± as in the male flowers; disk 5-angular or shallowly 10-lobed; staminodes small, subulate or occasionally staminiform; ovary c. 1.5 mm in diameter, 3-celled, subglobose, smooth; styles 3, 1 mm long, bifid, stigmas subulate.
Seeds c. 4 × 4 mm, broadly compressed-ovoid, foveolate; exotesta red, grey when dry, endotesta red or black.
A glabrous shrub or small tree up to 10 m tall, rarely taller, generally dioecious; branches horizontal.
Fruit 7 × 8 mm, (1)3-celled, 3-lobed to subglobose, smooth, green.
Bark smooth, grey, often with fine longitudinal markings.
Stipules 1 × 1 mm, triangular-ovate, subacute.
Petioles 3–7 mm long.
Twigs greenish.