Shrubs or trees, evergreen, perennial, dioecious; latex absent. Indumentum of simple multicellular trichomes, glandular trichomes absent, stinging trichomes absent. Stipules entire, inconspicuous, deciduous. Leaves alternate, petiolate, elobate, entire or toothed, penninerved, with a conspicuous pellucid dot in each areole. Inflorescences leaf-opposed [cf. subfam. description-Editor], cymose or fascicled, unisexual, with flowers in bracteate clusters. Male flowers pedicellate; calyx lobes 5 or 6, imbricate, free; petals absent; disc of numerous glands amongst stamens; stamens 6–60, filaments free; anthers dorsifixed, bilobate, thecae oblong and longitudinally dehiscent; pistillodes absent. Female flowers pedicellate; calyx lobes 5 or 6, imbricate, free; petals absent; disc annular; ovary 2-or 3-locular, ovules uniloculate; styles 2 or 3, united at base, bifid. Fruit capsular or rarely drupaceous, bi-or trilobate, surface smooth, dehiscing septicidally into 2 or 3 bivalved cocci. Seeds subglobose; testa fleshy; albumen fleshy; ecarunculate; cotyledons broad, flat.
Trees or shrubs, dioecious (very rarely monoecious); latex not evident; indumentum absent or short and simple. Leaves alternate; stipules small, connate, caducous, leaving annular scars at nodes; petiole short; leaf blade simple, entire or rarely sparsely serrulate, venation pinnate, usually pellucid-punctate. Inflorescence a leaf-opposed glomerule or cyme. Male flowers: sepals 5 or 6, free, imbricate, sometimes glandular abaxially; petals absent; disk extrastaminal or intrastaminal, annular or dissected; stamens 6-60, free; anthers longitudinally dehiscing; pistillode absent. Female flowers: sepals 4-8, imbricate, sometimes glandular abaxially; petals absent; disk annular; staminodes sometimes present; ovary (2 or)3(or 4)-locular; ovules 1 per locule; stigmas bifid (rarely multifid), spreading. Fruit a capsule or sometimes indehiscent and drupelike. Seeds not carunculate, covered by pale sarcotesta; endosperm present; cotyledon broad and flat.
Male flowers usually pedicellate; sepals (4)5–6(7), free, imbricate, unequal, glandular or not; petals absent; disk glands usually interstaminal, confluent; stamens 6–30 (African species), free, anthers dorsifixed, extrorse, longitudinally dehiscent at the back; pistillode absent.
Female flowers pedicellate; sepals (4)5–6(8), free, imbricate, subequal, glandular or not; petals absent; disk annular, sometimes lobed; staminodes 5–10; ovary 2–4-celled, with 1 ovule per cell; styles 2–4, united at the base, bifid or multifid, short.
Fruit 2–4-lobed or subglobose, dehiscing into bivalved cocci, loculicidal or indehiscent; exocarp smooth or reticulate; endocarp woody, coriaceous or crustaceous; columella persistent.
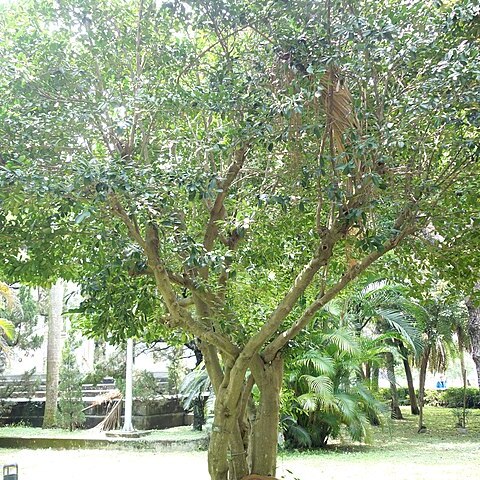
Leaves alternate, shortly petiolate, stipulate, simple, entire, denticulate or crenate-serrate, vesicular-punctate, penninerved.
Flowers fasciculate or glomerulate in leaf-opposed cymules, or subsolitary, somewhat gummy at first; bracts minute.
Seeds ecarunculate; exotesta pulpy; endotesta crustaceous; albumen fleshy; cotyledons broad, flat.
Dioecious, sometimes monoecious, usually glabrous trees or shrubs.
Stipules soon falling, leaving prominent scars.