Lianas or scandent shrubs. Leaves alternate, usually scabrous, pubescent with simple or stellate hairs more or less incrusted with silica, the petioles often canalic-ulate and narrowly alate. Inflorescences axillary or terminal, paniculiform, many-flowered. Flowers unisexual, actinomorphic, the pistillate with many apparently sterile hypogynous stamens; sepals usually 5, persistent, more or less equal or the outer slightly smaller; petals 2-5, caducous; stamens 50-200, multiseriate, persistent, the filaments free to basally fused, filiform, the anthers longitudinally dehiscent, the outermost frequently sterile, 2-thecate, the thecae nearly parallel to basally divergent, about half sunken into the dilated connective; carpels 1-5, pyriform, free, 1-loculed, the ovules 2-12, more or less erect on 2, seldom 3, ventral placentas, the styles filiform, exceeding the stamens in pistillate flowers, the stigmas capitate, frequently somewhat emarginate. Follicles 1-5, pyriform, dry, dehiscing along the ventral suture, the seeds 1-4, smooth, arillate, the aril lacerate, unilateral, about half enveloping the seed, the embryo small, straight.
Shrubs or climbers, rarely herbs or trees. Leaves petiolate; petiole often slightly grooved above; blade entire to denticulate, glabrous, tomentose or scabrid. Inflorescences few-to many-flowered terminal or axillary (usually from upper leaves) panicles. Flowers regular, hermaphrodite. Sepals 4–6(–15), imbricate, persistent, often reflexed in flower. Petals (2–) 3–5 (–6), usually white and showy, caducous, often emarginate. Stamens ∞, free; filaments thin at base, expanding towards apex; anther-thecae small and separated by the expanded connective, parallel, but more usually divergent towards their base, longitudinally dehiscent. Carpels 3–5, free; ovules usually numerous, more rarely reduced to 2, attached to the ventral suture; styles free, short; stigmas simple, only slightly differentiated from style. Fruit capsular, coriaceous, opening by the ventral and often the dorsal suture. Seeds 1–5, glossy, black in Africa, with a fimbriate or laciniate yellowish, reddish or purplish aril.
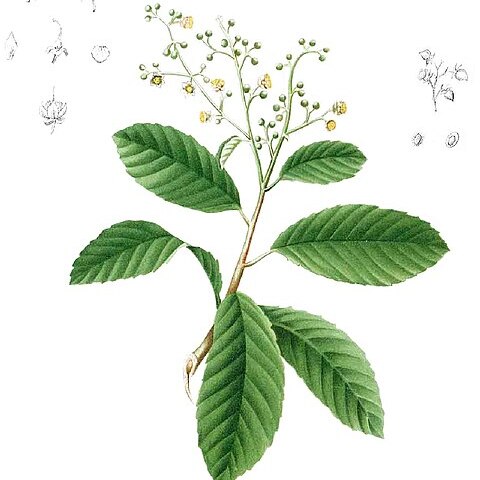
Shrubs, sometimes straggling, or lianas. Leaves simple, often scabrid on one or both sides. Petiole short, furrowed. Panicles axillary or terminal, few-to many-flowered. Flowers actinomorphic, fragrant. Sepals 4-5, persistent, often reflexed when in fruit. Petals 3-5, caducous, with emarginate apex, whitish or slightly reddish. Stamens ∞, with broadened connective, thereby anthercells divergent towards the base. Carpels 1-4, free, with a short style, ending in a simple stigma, with 4-20 ovules. Capsule coriaceous, opening with 1-2 longitudinal slits, ovoid with a short beak, one-to few-seeded. Seed glossy dark brown to black. Aril fleshy, cup-shaped, reddish or purplish, enveloping at least the base of the seed, equal-or unequal-sided with fimbriate or laciniate apical margin.
Evergreen shrubs or climbers. Leaves simple, alternate, petiolate; leaf blade scabrous or smooth, veins pinnate, secondary veins parallel, prominent, margin entire or smooth. Panicles terminal or axillary; bracts and bractlets linear. Flowers bisexual, small, 0.5-3 cm wide, actinomorphic. Sepals (3 or)4 or 5(-15), persistent in fruit, not accrescent, thinly leathery. Petals 3-5, white. Stamens numerous; anthers 2-loculed, with laterally expanded connective, dehiscing longitudinally. Carpels free, 1-5, on flat receptacle; ovules 2 to numerous per carpel. Follicles ovate, irregularly dehiscent. Seeds 1 to numerous, arillate; aril red or purple, fleshy, enclosing at least base of seeds.
Shrubs, small trees or lianes with entire or denticulate often scabrous leaves; stipules absent or represented by a narrow wing adnate to the petiole.
Stamens very numerous, dilated towards the apex, anther-thecae borne on the margins of the dilated connective parallel or divergent below.
Fruiting carpels brittle and woody or leathery when ripe, dehiscing along the ventral or along both sutures.
Carpels 3–5, free, each with a simple style; ovules few to many borne on the ventral suture of the carpel.
Sepals 5, convex, imbricate, persistent and becoming leathery in fruit.
Flowers moderate or large in terminal cymes, racemes or panicles.
Petals as many as the sepals or fewer, often emarginate.
Seeds few with a laciniate aril.