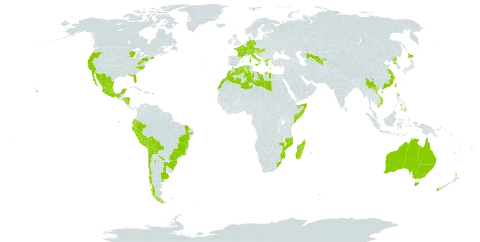
A large prostrate or prostrate-ascending somewhat succulent annual with stout trailing stems. Leaves 3-13 x 2-8.5 cm, rhombic, deltate or rhombic-ovate, obtuse or subacuminate at apex, with the base cuneate and more or less decurrent into the petiole, somewhat succulent; petiole 5-25 mm long. Flowers greenish or yellowish, solitary or paired, axillary, subsessile. Perianth-segments (3)4(5), up to 8 mm in fruit, acute, green outside, yellowish-green inside, unequal. Stamens 4-many, solitary or fasciculate, with orbicular anthers. Ovary semi-inferior, of 5-8 united carpels and 5-8 styles. Fruit up to 10 x 7 mm, smooth, conical or top-shaped, bearing below each perianth-segment a horn which sometimes gives rise to another flower or branchlet.
Stems mat-forming, 3-14 dm. Leaves 1-10 × 5-5 cm; petiole 1-3 cm, winged; blade pale green abaxially, dark green adaxially, midvein and lateral veins raised abaxially, ovate-rhombic to triangular, base truncate, papillate with larger papillae abaxially. Inflorescences: peduncle to 2 mm. Flowers sometimes unisexual; calyx lobes spreading, yellow, ovate to half orbiculate, 2 mm; stamens clustered or scattered. Fruits turbinate, 8-12 mm; horns 4-6. Seeds smooth. 2n = 32.
A perennial branched herb. It starts growing erect but after this lies over. It then grows along the ground. It grows to 12 cm high. The stems can spread out to 1 m along the ground. The leaves are small and thick on round fleshy stems. They are triangle shaped. They are 4-6 cm long. They have distinct veins underneath. The flowers are yellow and 8 mm across. They are hidden at the base of the leaves. The fruit is up to 1 cm long and with 4 or 5 horns on top.
Herbs annual, erect when young, becoming decumbent, 40-60 cm tall. Stems with densely placed bladder cells when young. Petiole 5-30 mm, thick; leaf blade rhomboid-ovate or deltoid-ovate, 0.4-10 × 2.5-8 cm. Pedicel to 2 mm. Flowers 1-3. Perigone tube 2-3 mm; lobes mostly 4, inside bright yellow to yellowish green. Stamens 10-13. Fruit turbinate, ca. 5 mm, 4-or 5-corniculate. Seeds as many as locules. Fl. and fr. Aug-Oct. 2n = 16*
Leaves 3–13 × 2–8·5 cm., rhombic, deltate or rhombic-ovate, obtuse or subacuminate at apex, with the base cuneate and more or less decurrent into the petiole, somewhat succulent; petiole 5–25 mm. long.
Fruit up to 10 × 7 mm., smooth, conical or top-shaped, bearing below each perianth-segment a horn which sometimes gives rise to another flower or branchlet.
Perianth-segments (3)4(5), up to 8 mm. in fruit, acute, green outside, yellowish-green inside, unequal.
A large prostrate or prostrate-ascending somewhat succulent annual with stout trailing stems.
Flowers greenish or yellowish, solitary or paired, axillary, subsessile.
Stamens 4-many, solitary or fasciculate, with orbicular anthers.
Ovary semi-inferior, of 5–8 united carpels and 5–8 styles.