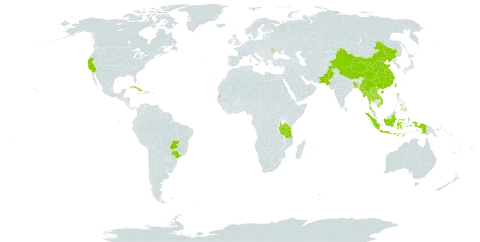
A grass which keeps growing from year to year. It grows to about 3 m tall. The stem is round and solid. The leaves are large and narrow. They are leathery and taper to a fine point. They are heart shaped at the base. The flower is brownish. The fruit is a grain. It is very small.