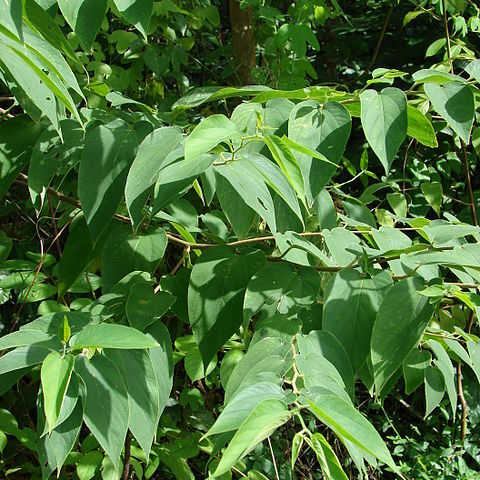
A straight slender tree. It grows to 10 m high. The trunk is 15-20 cm across. It may or may not lose its leaves during the year. The leaves have 3 conspicuous veins from the base. The leaves are heart shaped and with 3 veins. The leaves are often widest at the base. Leaves are often 6-15 cm long by 2.5-5 cm wide. There are fine teeth along the edge of the leaf. The leaves are rough and hairy when young. The flowers are small, green and no easily seen. They occur in short dense bunches. Mostly male and female flowers occur separately. The fruit are small and round and black. They are 4-6 mm across.
Tree to 30 m high. Leaves: lamina ovate to narrowly elliptic or lanceolate, 4–20 cm long, (1–) 1.5–8 cm wide, cordate or rounded, symmetrical or oblique base, serrate margin, attenuate at apex, usually coriaceous, markedly discolorous, scabrous above, velvety over hoary indumentum below; veins 4–8 pairs; petiole 2–20 mm long; stipules linear-lanceolate, 3–10 mm long. Inflorescence few-to many-flowered, to 4 cm long. Flowers globose, c. 2 mm diam.; perianth persistent. Drupe ovoid, c. 3–5 mm long, purple to black, calyx lobes persistent at base. See also Zich et al. (2020).
Tree or shrub, 1.5-18.0 m high, branches spreading or drooping. Bark smooth, grey, becoming longitudinally fissured, lenticels conspicuous, twigs densely pubescent. Leaves ovate-attenuate to ovate-lanceolate, base rounded to cordate, not crenate, rest of margins closely crenate, apex acute; midrib and veins compressed above, prominent below, lamina pubescent below. Inflorescence greenish cream-coloured; male, female and few bisexual; subtending bracts triangular. Tepals 1.0-1.5(-2.0) x 0.5 mm. Flowering time Oct.-Mar. Fruit purple or black, ovoid-globose, glabrous.
Leaves (4.5)6–11 x (1.5)2.2x5 cm. (juvenile leaves up to 15 x 9 cm.), attenuate-ovate to ovate-lanceolate or oblong-lanceolate; apex acuminate to attenuate; base rounded to cordate, ± asymmetric; margin evenly closely serrate from near the base; lamina ± scabrid, sparsely stiff-hairy (rarely glabrescent) above, ± densely pubescent to tomentose below, ± strongly 3-nerved from the base, midrib and lateral veins grooved above, prominent below; petiole 8–10( 13) mm. long; stipules 4–7 mm. long, lanceolate, pubescent, caducous.
Cymes 5–10 mm. long, many flowered; flowers mostly male with a few female (bisexual) flowers at the top, flowers greenish-cream; subtending bracts c. 1 mm. long, triangular; pedicels short or absent; sepals 1–1.5(2) x 0.5 mm.
Shrub or small tree, up to 12 m high. Leaf blade serrate almost from base, oblong-lanceolate to attenuate-ovate, (20-)75-140 x (12-)23-72 mm, rounded to cordate at base, penninerved. Stamens white. Flowers (perianth) green.
Shrub or small to medium tree up to 12 m. tall, deciduous; branches ± spreading; bark smooth, grey, lenticels conspicuous; twigs sparsely to densely pubescent.
Ovary pubescent, 1–1.5 mm. long; styles 0.5–1.2 mm. long, inrolled or divaricate, usually persistent.
Fruit drupaceous, purple or black, ovoid-globose, (2)3.5(4) mm. in diam. when dried, glabrous.