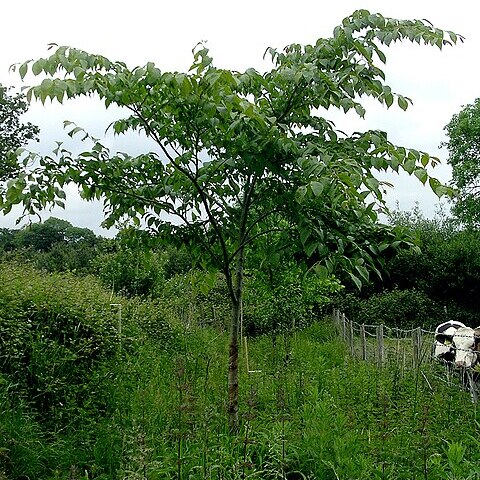
A medium sized tree. It loses its leaves during the year. It grows 10-20 m high. The current year's growth is softly hairy. Older branches have 2 corky wings. The leaves are broadly oval and 4-10 cm long by 2-6 cm wide. It has a tip at the end and is rounded at the base. There are double teeth along the edge. The flowers are in bunches on last year's growth. The fruit are winged seeds.