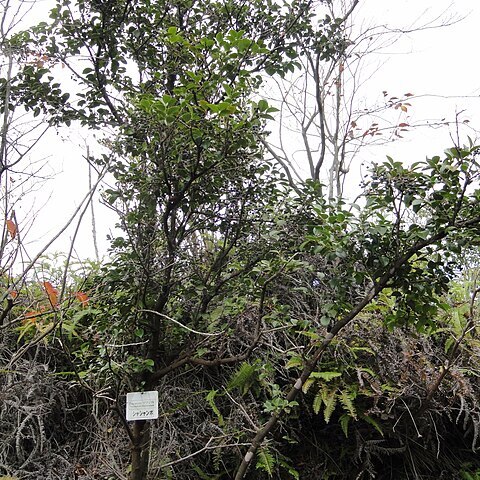
Shrub or small terrestrial tree, up to 6 m. Branchlets slender, tips greyish puberulent, older parts mostly early glabrescent. Leaves lax, lanceolate-oblong to elliptic-or ovate-lanceolate, variable in shape and size, rather long acuminate, acute, the tip with a sharp point, often somewhat curved, base acutely attenuate to the petiole, chartaceous to subcoriaceous, in erect reddish pink flushes when young, old ones withering red, light green, glabrous, finely though distinctly crenulate-serrate in general, rarely subentire, (3-)4—8 by (1.5-)2-3(-3.5) cm, midrib and nerves slightly prominent on both faces, sometimes puberulent as is the petiole, nerves 6-7 pairs, rather steeply ascending and anastomosing, reticulation lax, not much visible; petiole slender, 2-4 mm. Racemes from the upper axils, many-flowered, mostly greyish and shortly pubescent in all outer parts, glabrescent towards the fruiting stage; rachis slender, (2.5-)3-8 (in fruit up to 15) cm. Flowers fragrant, all set in a row and facing down. Pedicels 1-2 (-4, in fruit rarely up to 6) mm, bract foliaceous, small, subpersistent. Calyx tube cup-shaped, 1-1.5 mm, lobes triangular, acute, 1-1.5 mm. Corolla ur-ceolate-cylindric, slightly 5-angular, pink or white, pubescent on both sides, 5-6(-7) by 2.5 mm, lobes recurved, 1 mm. Filaments subulate, hairy below, 2-2.5 mm; anther-cells broad-oblong, base obtuse, almost 1 mm, whether or not minutely 2-spurred at the back; tubules slender, cylindric, c. 1.8 mm, opening by oblique short slits. Disk densely grey-pubescent. Style slender, glabrous, c. 5.5 mm. Berry globose, pubescent at the top, glabrescent elsewhere, reddish or finally dull purple or blackish, c. 4 mm ø.
More
Shrubs or small trees, evergreen, 2–6(–9) m tall, much branched. Twigs inconspicuously angled, pubescent or glabrous; bud scales inconspicuous. Leaves scattered; petiole 2–8 mm, puberulous or glabrous; leaf blade elliptic, rhombic-or lanceolate-elliptic, or lanceolate, rarely obovate, (1.1–)4–9 × (0.7–)2–4 cm, thinly leathery, glabrous, secondary veins 5–7 pairs, barely raised, fine veins conspicuous or not, base cuneate, broadly cuneate, or obtuse, margin plane, denticulate, apex acute, acuminate, rarely rounded or long acuminate. Inflorescences pseudoterminal, racemose, 4–10 cm, densely pubescent, rarely glabrous, many flowered; bracts persistent or caducous, leaflike, lanceolate, 0.5–2 cm. Pedicel ca. 4 mm, densely pubescent or subglabrous. Hypanthium densely pubescent or tomentellate, rarely subglabrous; calyx limb ca. 1 mm, triangular-toothed. Corolla white, rarely reddish, tubular or slightly urceolate, 5–7 mm, densely pubescent; lobes reflexed, triangular. Filaments 2–2.5 mm, densely pilose; anthers 2–2.5 mm, without spurs; tubules 2–2.5 × as long as thecae. Berry 10-pseudoloculed, dark purple, pubescent. Fl. Jun–Jul, fr. Aug–Oct.
An evergreen shrub. It grows 0.6-0.9 m tall. It spreads 0.6-0.9 m wide. It can be 3 m high. The branches are slender and grey but are red when young. The leaves are narrowly oval and have small teeth. The leaves are red when young and turn pale green. They are 5 cm long by 2 cm wide. The flowers are small and white or pink. There are often 10 flowers in a group. The fruit are red berries. The fruit are 5 mm across.