Leaves shortly petiolate or sessile; petiole glabrous to pubescent, up to 2 cm. long, those of a pair connate into a short ocrea, which is not widened into intrapetiolar stipules, with a single row of colleters in the axils; lamina usually pale green when plant in flower, when in fruit usually darker, especially above, herbaceous when fresh, membranous to papery when dry, variable in shape and size, elliptic or narrowly elliptic, 1·5–3·5(4) times as long as wide, 7–41·5 x 3–20 cm. (sometimes a little smaller), cuneate or decurrent into the petiole or base, not connate-perfoliate when sessile, acuminate with an often blunt apex or less often acute or obtuse in some leaves, glabrous on both surfaces to pubescent beneath all over and on the midrib above, with 8–22 secondary veins on each side; tertiary venation inconspicuous.
Calyx pale green (paler inside), 7–19 mm. long (when lobes erect), deciduous after the corolla has been shed and before the fruit develops, glabrous or puberulous, out and inside, inside with a zone of colleters from 1–2 mm. above the base of the tube to 1–2 mm. below the base of the lobes (the uppermost colleter near the edge of the base of the lobes and the remainder are arranged irregularly or in 1–3 rows above each other); tube cyathiform, 3·5–9 mm. long; lobes erect, 0·8–1·3 times as long as the tube, subequal, broadly ovate to oblong, 0·7–1·3(1·7) times as long as wide, 3·5–8 x 3·5–8 mm., obtuse, rounded, truncate, retuse, or emarginate at the apex, entire, imbricate in bud, usually partly recurved.
Trees to 10(-25) m tall. Bark pale gray-brown; branches lenticellate. Petiole short or absent; leaf blade obovate-oblong or obovate-elliptic, 7-41 X 3-20 cm, base cuneate or decurrent, apex obtuse or acute, glabrous on both surfaces or pubescent abaxially; lateral veins 8-22 pairs. Cymes 6-25 cm, usually many flowered. Calyx 0.7-1.9 cm, lobes broadly ovate to oblong. Corolla yellow or white, tube 0.7-1.5 cm, twisted; lobes obovate or elliptic, recurved, twisted in bud. Follicles obliquely subglobose, with pale green spots. Seeds dark brown, obliquely ellipsoid, 7-10 X 3.5-5 mm. 2n = 22.
A shrub or small tree. It grows 4-10 m tall. The trunk can be 2-30 cm across. The bark is smooth and pale grey. The leaf blade is pale green. The leaves vary in shape. There are many flowers in a loose group 4-16 cm long. The flowers have a bad smell. The fruit has 2 sections but only one develops. They are dark with pale green spots. They are 3-8 cm long by 3-8 cm wide and 3-7 cm thick. There are many dark brown seeds.
Carpels connected at the base only by an entire ring-shaped disk-like 0·8–1·2 mm. high incrassation and at the apex by the style; style split at the base, narrowly obconical, 4–8 mm. long, twisted and curled at the base, at the apex slightly narrower than the clavuncula; clavulcula 1–1·7 x 1–1·7 mm., with a ring of 1·7–3 mm. in diameter.
Fruit composed of two separate mericarps of which often only one develops; carpels dark and very pale, green-spotted, obliquely subglobose, often slightly wider than long and laterally compressed, 3–8 x 3–8 x 2·5–7 cm., 2-valved; wall 5–15 mm. thick, creamy inside and on section.
Stamens exserted for 0·5–1·2 mm. or occasionally just included, inserted 2–3 mm. below the corolla-mouth; anthers sessile, narrowly triangular, 4-5 x 1·3–2·5 mm., acuminate at the sterile apex and sagittate at the base, glabrous, usually twisted with the corolla.
Inflorescences usually long-pedunculate, 6–25 x 4–15 cm., usually many-flowered, fairly lax, 3·5–15·5 cm. long (incl. peduncle); peduncle pale green and glabrous to sparsely pubescent as branches and pedicels, usually slender; pedicels 3–20 mm. long.
Bracts deciduous, usually all shed before the first bud reaches full size, about as long as the calyx, ovate, obtuse, with a few persistent colleters at the edges of the axils; upper bracts often narrower; all bracts leaving conspicuous scars.
Seeds many, dark brown, dull, with orange aril, obliquely ellipsoid, 7–10 x 3·5–5 x 3–4 mm., laterally with 4–5 grooves, rough, minutely tuberculate.
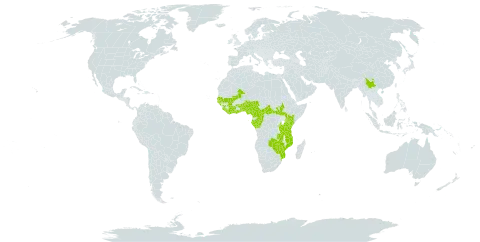
Trunk terete, 2–30 (40) cm. in diam., bark pale grey-brown, smooth or shallowly fissured near the base with some white latex.
Pistil glabrous, 7–12·5 mm. long (when style straightened out); ovary 1·6–2·5 x 1·7-3 x 1·2–2 mm., of two carpels.
Branches lenticellate; branchlets glabrous, puberulous, or pubescent, with more latex than in the bark.
Shrub-like tree or shrub 1–10(25) m. high.
Ovules about 200 in each carpel.
Flowers malodorous.