| Therapeutic use
|
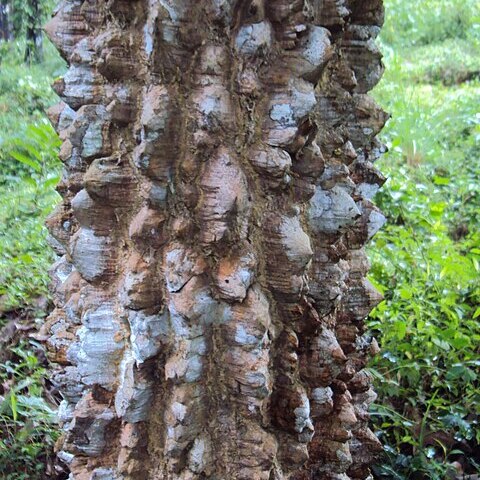
Anti-bacterial agents (bark), Cathartics (bark), Diuretics (bark), Hypoglycemia (bark), Parasympatholytics (bark), Toothache (bark), Typhoid fever (bark), Antifungal agents (bark), Aphrodisiacs (bark), Cholinergic antagonists (bark), Anesthesia (fruit), Anti-inflammatory agents (fruit), Antirheumatic agents (fruit), Aphrodisiacs (fruit), Appetite stimulants (fruit), Asthma (fruit), Astringents (fruit), Bronchitis (fruit), Central nervous system depressants (fruit), Cough (fruit), Diarrhea (fruit), Digestive system diseases (fruit), Dyspepsia (fruit), Fever (fruit), Mosquito control (fruit), Pharyngitis (fruit), General tonic for rejuvenation (fruit), Rheumatic diseases (fruit), Anthelmintics (fruit), Antinematodal agents (fruit), Anthelmintics (leaf), Insect repellents (leaf), Insecticides (leaf), Antipyretics (root), Cathartics (root), Kidney diseases (root), Menstruation-inducing agents (root), Hypohidrosis (root), Typhoid fever (seed), Digestive system diseases (stem), Hypotension (stem), Insect repellents (stem), Jaundice (stem), Skin diseases (stem), Anesthetic (unspecified), Antiseptic (unspecified), Asthma (unspecified), Bactericide (unspecified), Bronchitis (unspecified), Cholinergic (unspecified), Dyspepsia (unspecified), Heart (unspecified), Hyperglycemia (unspecified), Rheumatism (unspecified), Spasm (unspecified), Stimulant (unspecified), Toothache (unspecified), Astringent (unspecified), Cholera (unspecified), Medicine (unspecified), Digestive (unspecified), Inflammation (unspecified), Dermatitis (unspecified), Anti-infective agents, local (unspecified), Antirheumatic agents (unspecified), Appetite stimulants (unspecified), Astringents (unspecified), Disinfectants (unspecified), Heart diseases (unspecified), General tonic for rejuvenation (unspecified), Anti-bacterial agents (whole plant), Antifungal agents (whole plant)
|