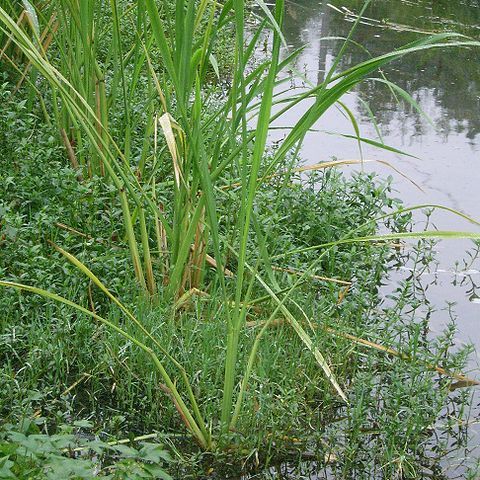
Robust, stout perennials, to 3 m, with strong rhizomes and large, rather narrow, purplish panicle. Cataphylls broad. Leaf-sheath glabrous, many-nerved, spongy and honey-combed with numerous transverse septa beneath the stiff epidermis, pale greenish, straw-coloured or light brown to purplish; margins papery. Ligule 25-40 mm, nerved, smooth, acute, entire or later fimbriate. Collar conspicuous abaxially and separating sheath and blade. Leaf-blade 50-120 × 1-2.5 cm, linear-lanceolate, light green, tough, midnerve much thickened abaxially below, glabrous, margins scabrid; tip pungent. Culm to 2 cm diam., internodes glabrous. Panicle 30-70 cm, with sparsely scabrid pulvinate branches with long white hairs in axils, all branches and spikelets ascending, upper branches with ♀ spikelets, pedicels slender, capillary, tips cupule-like equally wide, sometimes short-ciliate; lower branches with ♂ spikelets and also ♂ spikelet at times among ♀ spikelets in middle branches. ♂ spikelets: lemma 12-15 mm, nerves 7, raised, purplish, linear-lanceolate, membranous, very finely scabrid on and between nerves, long-acuminate to shortly (c. 2 mm) awned. Palea c. 10.5 mm, 3-nerved, sparsely scabrid on keel and between nerves above, margins wide, hyaline. Lodicules 0.75 mm. Stamens 6; anthers (5)-6-7 mm, bright orange-yellow, tailed. ♀ spikelets: lemma 15-20 mm, 7-nerved, linear, chartaceous, greenish to sometimes slightly purplish, scabrid on nerves and very finely scabrid between nerves, awn scabrid, erect 12-30 mm. Palea 10-13 mm, 3-keeled, nerves scabrid, interkeels faintly scabrid. Gynoecium: ovary 1.5 mm, beaked; stigma-styles c. 20 mm, stigma white exserted beyond lemma apex. Caryopsis c. 6 × 1.5 mm. Fig. 3.
More
Perennial, rhizomatous. Culms erect, 1–2.5 m, ca. 1 cm thick, rooting at lower nodes, nodes glabrous. Leaf sheaths longer than internodes, thickened, lower sheaths tessellate; leaf blades broadly linear, 50–90 × 1.5–3.5 cm, abaxial surface scabrous, adaxial surface glabrous, tapering to base, apex abruptly narrowed to a long point; ligule triangular, 1–1.5 cm. Panicle 30–50 × 10–15 cm, lower branches with male spikelets, upper branches with female spikelets, middle branches mixed; branches semiverticillate, many at each node, sparsely spinulose; pedicel apex disk-shaped with spinulose margin. Male spikelet 0.8–1.5 cm; lemma elliptic-oblong, margin ciliate; awn 2–8 mm, scabrous; anthers 5–8 mm. Female spikelet 1.5–2.5 cm; lemma linear, scabrous on veins; awn 1.5–3 cm, scabrous. Caryopsis ca. 1 cm. Fl. and fr. Jun–Sep. 2n = 30, 34.
A grass which grows in water. It keeps growing from year to year. It grows 1.2 m tall. It has stout rhizomes or underground stems buried in the mud. The internodes near the base are 6-8 cm long by 2 cm wide. The leaves are crowded towards the base of the plant. The leaf blade is 70-130 cm long by 2-3 cm wide. The stems become swollen as the result of infection by a smut fungus. They are like a stubby bamboo shoots. They are harvested before the black fungus spores develop.