Morphological characters and geographic distribution are the same as those of the family.
Characters as for family.
Characters of the family.
| Life form | perennial |
| Growth form | |
| Growth support | - |
| Foliage retention | evergreen |
| Sexuality | hermaphrodite |
| Pollination | - |
| Spread | - |
| Mature width (meter) | - |
| Mature height (meter) | - |
| Root system | - |
| Rooting depth (meter) | - |
| Root diameter (meter) | - |
| Flower color | - |
| Blooming months | - |
| Fruit color | - |
| Fruiting months | - |
| Nitrogen fixer | - |
| Photosynthetic pathway | - |
| Light | - |
| Soil humidity | - |
| Soil texture | - |
| Soil acidity | - |
| Soil nutriment | - |
| Hardiness (USDA) |
| Uses | - |
| Edible | - |
| Therapeutic use | - |
| Human toxicity | - |
| Animal toxicity | - |
| Mode | - |
| Germination duration (days) | - |
| Germination temperacture (C°) | - |
| Germination luminosity | - |
| Germination treatment | - |
| Minimum temperature (C°) | - |
| Optimum temperature (C°) | - |
| Size | - |
| Vigor | - |
| Productivity | - |
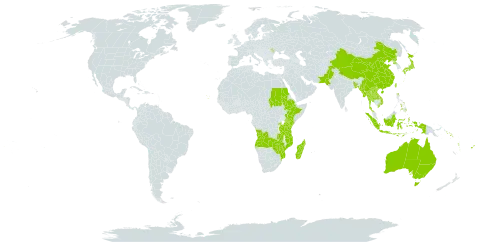
| LSID | urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:331330-2 |
| WFO ID | wfo-4000001081 |
| COL ID | 8VTHW |
| BDTFX ID | - |
| INPN ID | 672348 |
| Wikipedia (EN) | Link |
| Wikipedia (FR) | Link |