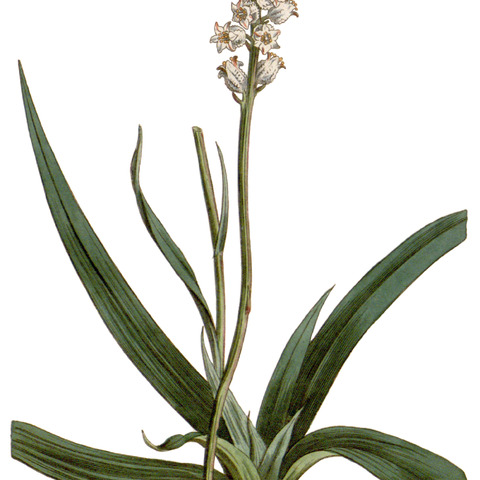
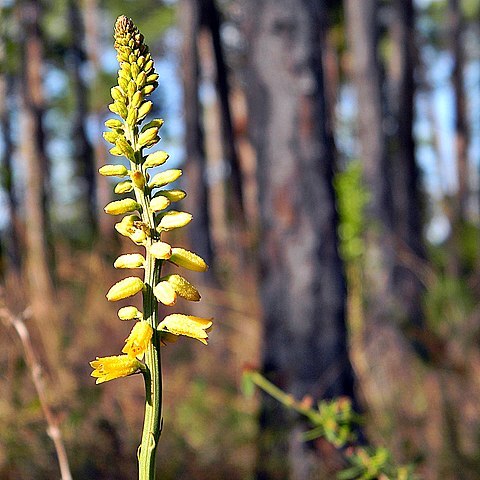
Herbs, perennial, scapose, rhizomatous. Leaves in dense basal rosettes, clasping erect branches; blade narrowly linear to lanceolate, oblanceolate, linear-elliptic, or elliptic, flat, leathery, distal margins fused to form subulate tips. Scape 2–10 dm. Inflorescences racemose. Flowers each subtended by 2 subulate, unequal bracts, short-pedicellate; perianth white, yellow, or golden orange, cylindrical, campanulate, or obovoid, abaxial surfaces rough; tepals 6, connate basally; stamens 6, included; filaments adnate to perianth; anthers oblong-lanceolate, longer than filaments; ovary half inferior with proximal portions of perianth adnate at maturity; style 3-branched at apex. Fruits capsular, 3-locular, beaked. Seeds amber, deeply sulcate, ellipsoid to ovoid, 0.5–0.8 mm, lustrous.
Erect, stemless, rhizomatous herbs. Roots fibrous. Leaves basal, linear or lanceolate, sessile, the veins of the decayed bases persisting as fibres at the base of the plant. Inflorescence a raceme or spike. Flowers solitary in the axils of the bracts, with a single bracteole. Pedicels not articulated. Perianth segments connate at the base, equal, with three (often indistinct) veins, ascending or reflexing, glabrous or pubescent, white or pink. Filaments subulate, shorter than and attached to perianth; anthers dorsifixed, oblong to ovoid, dehiscing introrsely. Ovary half-inferior, 3-celled; ovules axile, numerous; style simple or minutely 3-lobed. Fruit a capsule; perianth persistent. Seeds oblong.