Tree up to 40 m tall, deciduous. Leafy twigs 1.5-5(-8) mm thick, densely brown to yellowish (patent to appressedly) puberulous often intermixed with longer brown uncinate hairs, smooth, drying brown (to blackish); with or without up to 5 mm long short-shoots on the older wood. Leaves distichous; lamina subcoriaceous to chartaceous, entire or pinnatifid to 3-lobate when juvenile, basally attached (or occasionally peltate), elliptic (to subrotundate), (3-)10-30(-33) by (2-)6-17 cm, apex acuminate, base cordate to subcordate to rounded (to obtuse to subcuneate), often slightly unequal, margin denticulate towards the apex, particularly the acumen, sometimes entire, ± revolute (at least towards the base); upper surface brownish to whitish puberulous to subtomentose (mainly) on the main veins, smooth (occasionally ± scabrous or ± minutely bullate); lower surface brownish to whitish patent to appressedly puberulous to subtomentose or to hirtellous on the veins, smooth (to scabridulous); lateral veins (6-)10-20 pairs, in the lower part of the lamina usually faintly loop-connected, the lower ones spaced or ± crowded (2 or 3 pairs departing close together), none (or sometimes one or a few) branched or forked away from the margin, tertiary venation scalariform, ± prominent; petiole (0.5-)0.8-2(-3) cm long, 1.5-3(-4) mm thick, brown puberulous and often intermixed with longer uncinate hairs, the epidermis persistent (or flaking off); stipules lateral, 0.3-0.5(-1) cm long, brownish to whitish puberulous, caducous (or subpersistent), or persistent, at the shoot-apices forming the terminal buds (or also in the leaf axils and forming the lateral buds). Staminate inflorescences axillary (or just below the leaves), solitary, or 1-5 on short-shoots on the older wood, patent or deflexed; peduncle 3-35 mm long, densely brown puberulous; head subglobose to ellipsoid, to clavate (or to pulvinate), to 3 cm long, 3-15 mm diam.; perianth with 2 or 3 free tepals; stamen 0.5-0.8 mm long, anther 0.1-0.2 mm long; interfloral bracts peltate, the apical part c. 0.3 mm diam., puberulous, caducous or persistent. Pistillate inflorescences axillary or below the leaves (down to previous season’s growth), solitary; peduncle (5-)10-80 mm long, minutely brown velutinous; head subglobose to obovoid; perianth minutely puberulous; stigma simple; interfloral bracts peltate, caducous (or persistent), the apical part c. 0.3 mm diameter. Infructescences to c. 7 cm diam., often ± lobed, green to orange with pink to red flesh, surface minutely velutinous; fruits ellipsoid, 1-1.2 cm long.
More
A large tree which loses its leaves during the year. The tree grows to 10-50 m high. The trunk is short and erect but is can be bent. The crown is rounded and spreading. The bark is reddish-brown and rough and scaly in old trees. The young branches are densely covered with stiff, pale brown hairs. The leaves are alternate. The leaf stalk is 2-3 cm long. The leaves are oblong and 20-30 cm long and 2-16 cm wide. Sometimes the leaves have lobes. They are dark green and smooth above but softly hairy underneath. Male and female flowers occur on the same tree. They are clustered together in the outer surface of rounded heads. These grow at the base of the leaves. The male flower head is yellow. They are 0.8-5 cm long but fall off. The fruit have a fleshy receptacle. The fruit are velvety and yellow when ripe. They are 7-13 cm across. The fruit contains 20-30 seeds. The seeds are oblong.
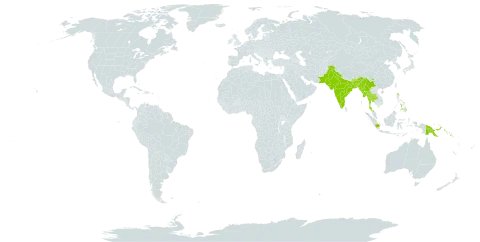
It is a tropical plant. It suits a warm, humid climate. It grows in Nepal from sea level to 900 m altitude. In China it grows in forests in limestone mountains between 100-700 m altitude in Yunnan. In India it grows up to 1,500 m altitude. It is sensitive to frost, but is hardier than jackfruit. It can grow in arid places.
More
Forests on limestone mountains at elevations of 100-1,300 metres in southern Yunnan. Evergreen, semievergreen and moist deciduous forests at elevations up to 1,800 metres.