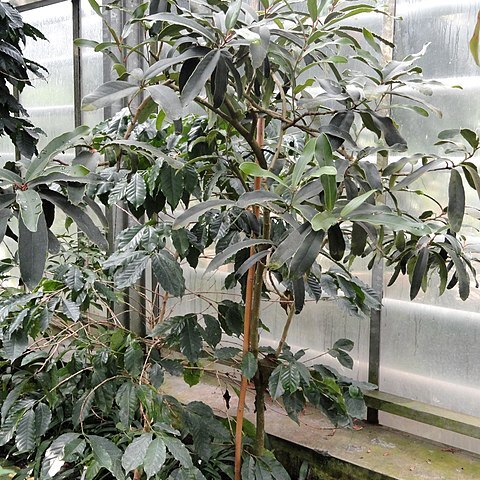
An evergreen shrub or small tree. It is dense, with many branches. It is mostly only 2-3 m high. The bark is grey with stripes. The leaves are alternate and vary in shape. They are narrow and oblong. They are 3.5-14 cm long and thickly leathery. The flowers are white large and with 5 spreading petals. These tend to curve backwards. These can be 2 cm long. The flowers occur in loose clusters. They are mostly in leaf axils but sometimes on old wood. The fruit are long and narrow and woody. They are 9 cm long with 5 ridges. The fruit can float in the sea for months and the seed remain viable. They contain many seeds.
Leaves evergreen; petiole 1–2 cm. long; lamina 3·5–35 x 2–7·6 cm., very variable in shape, those on young shoots narrowly oblong to oblong-linear with margin spinose-dentate, those on mature shoots narrowly to broadly obovate with margin crenate to entire, all rounded to retuse at the apex, cuneate to rounded at the base, coriaceous; stipules subulate.
Inflorescence (l)3–12(17)-flowered, pedunculate, in leaf axils; peduncle 1–9 cm. long, usually ± flattened, 1·5–5 mm. wide, sometimes bearing at the apex 1–2 leaf-like bracteoles c. 1 x 1 cm.; bracteoles otherwise small, scale-like, deciduous; pedicels 0·6–1·8 mm. long.
Drupe 4–10 x 1·9–3 cm., ovoid to oblong-fusiform or cylindric, prominently 5-ribbed (in our area), with mesocarp woody at first but said to become eventually pulpy and edible.
Seeds 4·5–7·5 x 3–3·5 mm., brown or blackish, irregularly compressed-ellipsoid, carinate, minutely rugulose in ridges.
Sepals c. 2·5 x 3·5–4 mm., united in the lower 1/2, with lobes triangular-oblate, apex rounded, margin entire.
Shrub or small tree, (2)3–7(10) m. high, much branched; stems smooth, angular when young, later terete.
Petals greenish-or yellowish-white, 1·2–1·7 x 0·9–1·2 cm., broadly oblong-ovoid, obtuse, ± fleshy.
Stamens with filaments c. 1·2 mm. thick; anthers c. 5 x 2·5 mm.
Ovary 5-angled, c. 8–10 mm. long including style.
Disk-lobes with filaments 4–6, linear, unequal.