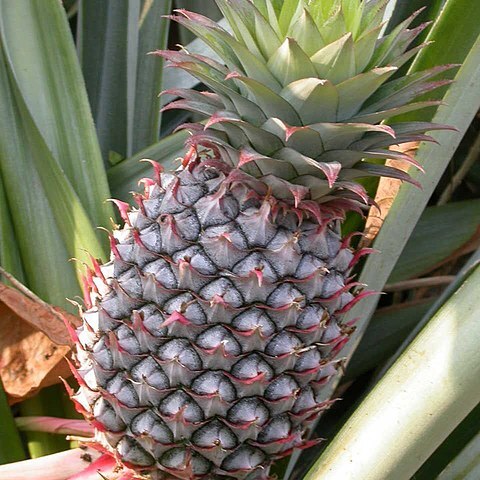
Perennial herbs or shrubs, sometimes rhizomatous, bisexual. Leaves in a rosette, alternate or distichous; lamina with specialised absorptive scales; margins often spiny; stipules absent. Flowers actinomorphic or (not in Australia) zygomorphic, in racemes, spikes or solitary, lateral or terminal. Sepals 3, free or united. Petals 3, free or (not in Australia) united, with or without basal scales. Stamens 6 in 2 series of 3, free or united or epipetalous; anthers bilocular, opening by longitudinal slits. Ovary hypogynous or epigynous, 3-locular, 3-carpellate; style 1, 3-branched; placentation axile; ovules numerous. Fruit a septicidal capsule, synangium or (not in Australia) berry. Seeds with or without a plumose appendage or (not in Australia) winged; embryo small, at base of copious starchy endosperm.
Herbs, perennial, terrestrial, among or on rocks, or epiphytic. Roots usually present, often poorly developed in epiphytic taxa. Stems very short to very elongate. Leaves usually spirally arranged, forming water-impounding rosette, occasionally lax and / or 2-ranked, simple, margins serrate or entire, trichomes nearly always covering surface, peltate, water-absorbing. Inflorescences terminal or lateral, sessile to scapose, simple or compound; bracts usually present, conspicuous. Flowers bisexual or functionally unisexual, radially symmetric to slightly bilaterally symmetric; perianth in 2 distinct sets of 3; stamens in 2 series of 3; ovary inferior or superior; placentation axile. Fruits capsules or berries. Seeds plumose, winged, or unappendaged.
Stamens 6, mostly inserted at the base of the segments, free or partially adnate to them; anthers free or rarely connate in a ring, linear, usually versatile, 2-locular, opening by longitudinal slits
Perianth hypogynous to epigynous, segments in two series, the outer calyx-like, imbricate, the inner corolla-like and free or variously connate, imbricate
Leaves usually in a dense cluster, long and strap-shaped, rigid and spinulose-toothed or rarely flaccid, often coloured towards the base
Flowers in a terminal head, spike, or panicle often with highly coloured bracts, actinomorphic, bisexual or rarely unisexual
Fruit fleshy and indehiscent or rarely opening unevenly, or rarely a septicidal or loculicidal capsule
Ovary superior to inferior, 3-locular; style slender, elongated, stigmas 3
Seeds with abundant mealy endosperm and a small embryo, sometimes winged
Ovules numerous in each loculus, the axile placentas sometimes divided
Mostly short-stemmed epiphytes or growing on rocks