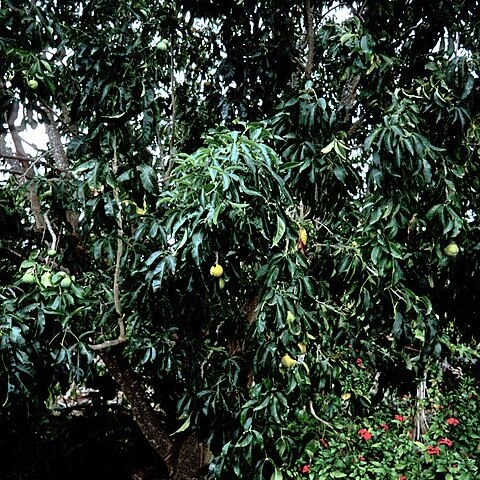
Medium-sized or large tree 3–12 m. in East Africa.. Leaves digitately (3–)5-foliolate; leaflets petiolulate, elliptic or elliptic-oblong to ovate, sometimes puberulent on petiole and petiolules, translucently gland-dotted.. Flowers white or greenish white in axillary panicles.. Fruit resembling an apple, 8–10 cm. in diameter, yellowish.