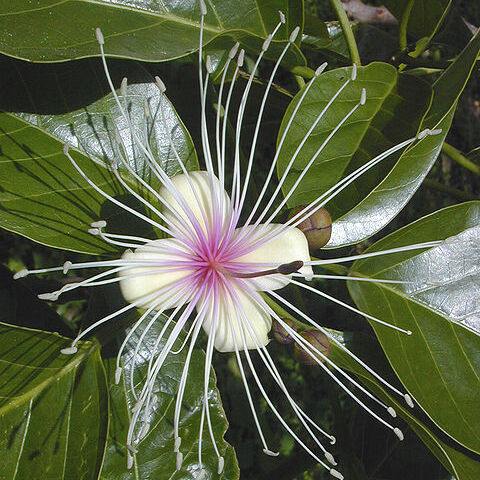
Trees 3-15 m tall, to 40 cm d.b.h. Twigs light greenish to yellowish green when dried, with gray elongated lenticels. Petiole (5-)6-7(-10) cm, adaxially with minute triangular glands near rachis; petiolules 3-5(-7) mm; leaflet blades (4-)5.5-7(-10) × (2-)3-4 cm, 2-2.5 × as long as wide, thin and leathery, abaxially gray, adaxially dull green, midvein reddish, secondary veins 5-10 on each side of midvein, reticulate veins obvious, apex acuminate to abruptly acuminate. Inflorescences racemes or corymbs, 10-25-flowered, with branchlet just below flowers having fewer leaves; axis 3-7 cm, after flowering little elongated, often marked with pedicel scars; bracts 0.8-1.5 cm, leaflike or slender, caducous. Flowers open as leaves emerge. Pedicel 2-5[-9?] cm. Sepals ovate, 2-4.5 × 1.5-3 mm, apex acuminate. Petal white to yellow, claw 3.5-5 mm, blade 1.5-2.2 cm. Stamens 16-22[-30]; filaments 3-6 cm; anthers 2-3 mm. Gynophore 3.5-6.5 cm; ovary ovoid to subcylindric, 3-4 × 1-2 mm. Fruit ovoid to obovoid, 1.8-2.6[-3.5] cm; pericarp 5-10 mm thick, apically scabrous and gray to dust-colored with nearly circular ash-yellow flecks; stipe 2.5-3 mm in diam., thickened, woody. Seeds 25-30 per fruit, dark brown, 1.2-1.8 cm, tuberculate. Fl. Mar-May, fr. Jul-Aug(-Oct). 2n = 26.
Tree to 30 m tall. Leaves trifoliolate; leaflets subsessile, herbaceous, variable, mostly obovate, acute, 5.5–18 cm long, 2.5–7 cm wide, with 7–11 pairs of nerves; base acuminate; petiole to 10 cm long, glands small, triangular or absent. Inflorescence terminal on leafy twigs. Sepals ovate, 4–10 mm long. Petals white to orange; claw 5–20 mm long; lamina elliptic to broadly ovate, the upper 2–4.5 cm long, the lower pair 1.5–3 cm long. Stamens 10–30; androgynophore 1–4 mm long; filaments red, to 11.5 cm long. Gynophore red, 4–7 cm long; ovary cylindrical-ovoid, 4–6 mm long. Fruit elongate to subglobose 3–20 cm long, 3–9.5 cm wide; pericarp white and smooth becoming papillate and yellow-grey when older. Seeds somewhat flattened, cordate, axis through attachment 5–17 mm long, 4–8 mm thick, usually with a tuberculate dorsal keel, sides smooth to grooved.
An evergreen or deciduous tree. It grows up to 7-15 m tall and 45 cm across the trunk. The tree spreads to 2-4 m across. The stem is erect and the bark is smooth, with branches low down. The leaves have long petioles, 2-9 cm long. The leaves are divided into 3 leaflets growing from the same point. The leaflets are pointed at the base and have a slender point at the tip. The two halves of the leaflets are unequal in size. The leaflets are 5-27 cm long by 3-10 cm wide. The leaves are light green. The flowers are white, then yellow, turning pale violet and they are large, up to 5-7 cm across. They are borne in large bunches 3-14 cm long. These are near the ends of branches. The fruit is rounded and about 6-15 cm long by 5-9 cm across. They are sausage shaped. The fruit is edible. There are many seeds, which are kidney shaped.