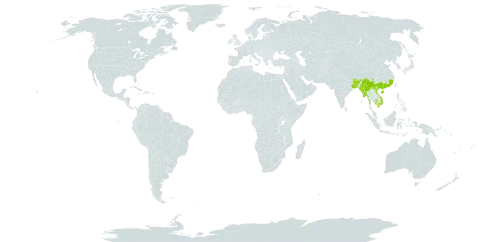
Trees 5-10(-20)[-30] m tall. Twigs grayish brown, often hollow, with sparse whitish lenticels. Petiole (3-)5.5-9 cm, glands adaxially toward rachis; petiolules (2.5-)4-7 mm; leaflet blades elliptic, (6.5-)8-10 × 3-4(-5) cm, 2-2.5 × as long as wide, subleathery, glossy, abaxially drying gray, adaxially drying to brown, midvein reddish, secondary veins 5-8(-10) on each side of midvein, apex acuminate to abruptly acuminate. Inflorescences racemes or corymbs, 13-25(-35)-flowered, with a few leaves on basal part; rachis (2-)3-5(-7) cm, after flowering with little increase in length, often with pedicel scars. Pedicel 2-4 cm. Sepals linear to narrowly lanceolate, (3-)4-6 × 2-3 mm. Petal white to creamy but drying pinkish, claw 3-7 mm, blade 1.4-2.4 cm. Stamens 16-20; filaments (2-)3-4.5 cm; anthers 2-3 mm. Gynophore 4-6 cm; ovary oblong-ellipsoid, 3-4 × 1-2 mm. Fruit globose, 3-4 cm; pericarp 2-3 mm thick, apically scabrous, with nearly circular small ash-yellow flecks; stipe 3-7 mm in diam., thickened, woody. Seeds 30-50 per fruit, dull brown, lens-shaped, 8-10(-12) × 4-10 mm, smooth. Fl. Mar-Jul, fr. Jul-Aug.
More
A tree. It loses its leaves during the year. It grows 5-10 m tall. It can be taller. The leaves have narrowly oval leaflets. They are 6-10 cm long by 2-3 cm wide. There are 13-25 flowers in a group. The fruit are 3-4 cm across.