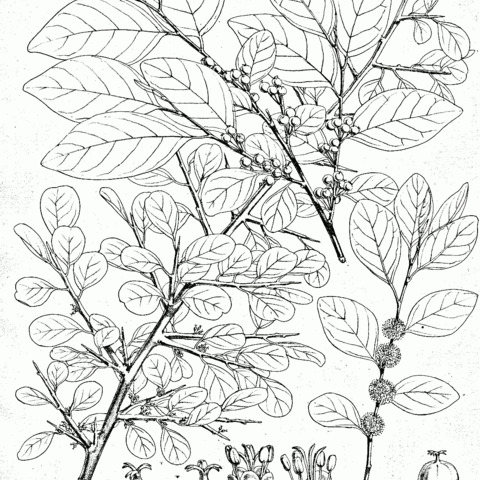
Dioecious or rarely monoecious trees or shrubs, usually without indumentum. Leaves alternate, shortly petiolate, stipulate, simple, entire, penninerved. Flowers axillary, usually in the proximal axils of leafy branches, the males numerous, fasciculate, the females few or occasionally solitary. Male flowers: pedicels capillary; sepals (4–)5(–7), unequal, imbricate; petals 0; disc-glands (4–)5(–7), interstaminal, alternating with the sepals; stamens (4–)5(–7), filaments free, anthers extrorse, longitudinally dehiscent; pistillode usually large, deeply 2–3-partite, the divisions often appendiculate or bilobate. Female flowers: pedicels and sepals as in the ♂ flowers; petals 0; disc flat, annular, entire or shallowly 5–6-lobed; ovary smooth, (2–)3(–4)-locular, with 2 ovules per locule; styles (2–)3(–4), connate at the base, recurved or spreading, bifid or bilobate. Fruit slightly or scarcely fleshy, usually loculicidally dehiscent; endocarp crustaceous, 3-locular or rarely 2-or 1-locular by abortion. Seeds 2 per locule, trigonous, dorsally convex, often invaginated, usually smooth, ecarunculate; testa fairly thick, crustaceous; albumen rather scanty; embryo usually incurved; cotyledons ovate, elliptic or obovate, flat.
Shrubs [trees], usually dioecious, rarely monoecious, glabrous [pubescent, hairs simple]; branching not phyllanthoid. Leaves deciduous [persistent], alternate, simple, all well developed; stipules deciduous [persistent]; blade margins entire. Inflorescences unisexual, fascicles [racemes or panicles, or pistillate flowers solitary]. Pedicels present. Staminate flowers: sepals [4–]5[–7], distinct; petals 0; nectary extrastaminal, [4–]5[–7] glands [annular, lobed]; stamens [4–]5[–7]; filaments distinct; connectives not extending beyond anthers; pistillode [2–]3-divided nearly to base [absent]. Pistillate flowers: sepals persistent, [4–]5[–7], distinct; petals 0; nectary annular, entire [angled or lobed]; pistil [2–]3[–4]-carpellate; styles [2–]3[–4], connate proximally, 2-fid. Fruits berries [capsules]. Seeds 2 per locule, rounded-trigonous; seed coat dry, reticulate or finely verrucose [smooth]; caruncle absent. x = 13.
Seeds 2 per locule, or 1 by abortion, trigonous, dorsally convex, hilum often invaginated, ecarunculate; testa smooth or occasionally reticulate or verruculose, thick or thin, crustaceous; albumen scanty or copious; embryo straight or curved; cotyledons ovate, elliptic or obovate, flat, longer than the radicle.
Male flowers: pedicels capillary; sepals (4)5(7), unequal, imbricate; petals absent; disk glands (4)5(7), interstaminal, alternating with the sepals; stamens (4)5(7), filaments free, anthers extrorse, longitudinally dehiscent; pistillode usually large, 2–3-partite, the arms often appendiculate or 2-lobed.
Female flowers: pedicels and sepals as in the male ; petals absent; disk flat, annular, entire or shallowly 5–6-lobed; ovary smooth, glabrous, (2)3(4)-locular, ovules 2 per locule, hemitropous; styles (2)3(4), connate at the base, recurved or spreading, bifid or 2-lobed.
Fruit 3-lobed (4-lobed)-subglobose, fleshy and indehiscent or dry and loculicidally dehiscent; exocarp fleshy or thin; endocarp crustaceous, 3-locular or rarely by abortion 2-or 1-locular; columella persistent (not persistent in African taxa).
Leaves alternate, shortly petiolate, stipulate, simple, entire, penninerved, usually deciduous.
Flowers axillary, the males numerous and fasciculate, the females few or solitary.
Dioecious, or rarely monoecious, usually glabrous trees or shrubs.