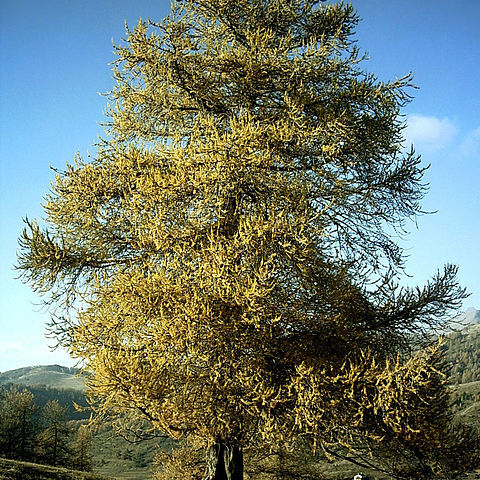
Trees deciduous; crown sparse, open. Bark silver-gray to gray-brown on young trees, becoming reddish brown to brown, smooth initially, scaly to thickened and furrowed with age. Branches whorled; short (spur) shoots prominent on twigs 2 years or more old, each bearing leaves (needles), and often pollen cone, or seed cone; lateral long shoots (sylleptic branches) sometimes produced by current-year growth increments; leaf scars many. Buds rounded. Leaves in tufts of 10--60 on short (spur) shoots or borne singly on 1st-year long shoots, deciduous, ± flattened, with abaxial keel, sessile, base decurrent, sheath absent, apex pointed or rounded; resin canals 2. Pollen cones solitary, ovoid-cylindric, yellowish. Seed cones maturing in 1 season, persisting several years, erect, globose to ovoid, usually terminal on short shoots and thus appearing stalked, sometimes sessile on 1-year-old long shoots; scales persistent, circular to oblong-obovate, thin, lacking apophysis and umbo; bracts included or exserted. Seeds winged; cotyledons 4--6. x =12.
Deciduous, scarcely resinous trees; branches irregularly whorled, somewhat horizontal; bark becoming thick and furrowed. Winter buds small, subglobose, not resinous. Long shoots with spirally arranged, solitary lvs; short spur-like shoots with fascicles of up to c. 50, fine, soft, flattened to nearly quadrangular, grass-green lvs; resin ducts 2. ♂ strobili (cones) terminal on short shoots, oblong to globose, yellow, at anthesis before lvs. ♀ cones terminal on short shoots, ripening in first year, erect to downward pointing, surrounded by basal ring of brown, fimbriate, hair-like scales; bract scales much > ovuliferous scales at anthesis, red, purple or green, usually included in mature cone; ovuliferous scales becoming semi-woody, persistent; ovules 2 to each scale. Mature cones not disintegrating, few to numerous along branchlets. Seed with large wing.
Male and female cones sessile or subsessile on leafless dwarf branches of previous year’s growth, globose or subglobose; lvs deciduous, needle-like; branches of 2 sorts, (1) long shoots of the current year, with scattered lvs, and (2) dwarf branches produced laterally on the previous year’s growth, slowly elongating for many years and producing crowded clusters of numerous lvs. 10, mainly N. Temp.