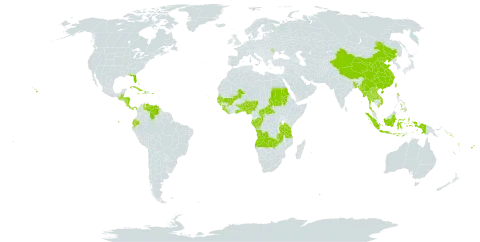
Trees, shrubs or less often lianes, with mostly glabrous, less often hairy or tomentose stems. Stipules leafy, undivided, free or forming a sheath with the petioles. Leaves opposite or rarely in whorls of 3, sometimes only 1 at flowering nodes. Flowers heterostylous (? always), hermaphrodite or rarely unisexual, in tight capitula, the flowers usually joined, at least by the bases of the calyces, the capitula sometimes bearing single large coloured bracts or occasionally many smaller bracts; capitula 1-several at the nodes, frequently arranged in umbels, pedunculate or rarely sessile. Calyx-tube urceolate or hemispherical, the limb short, truncate or obscurely to distinctly toothed, persistent. Corolla ± coriaceous, funnel-shaped or salver-shaped; lobes (4–)5(–7), valvate; throat glabrous or pilose. Stamens (4–)5(–7), inserted in the throat; filaments short; anthers and style included or exserted. Disc swollen or annular. Ovary 2–4-locular, sometimes imperfectly so; style with 2 short to long linear branches; ovules solitary in the locules, attached to the septum below the middle or near the base, ascending, anatropous or amphitropous. Fruit syncarpous (very rarely scarcely so), succulent, containing several pyrenes; pyrenes cartilaginous or bony, 1-seeded or joined into a 2–4-locular woody structure. Seeds obovoid or reniform, with a membranous testa and fleshy endosperm.
Shrubs or small trees. Leaves opposite, occasionally ternate, petiolate; stip-ules interpetiolar, connate, persistent, usually bifid. Inflorescences terminal or axillary, the peduncles present or absent, the flowers in small heads. Flowers with hypanthium and calyx of adjacent flowers partially or completely united; calyx truncate, the teeth obscure; corolla infundibuliform or hypocrateriform, the lobes 4-7, valvate; stamens 4-7, the anther connectives produced at the apex; ovary 2-4-celled, each with an ascending ovule attached near the base of the cell. Fruit a syncarp, often large, fleshy and white, each cell with a 2-celled pyrene.
Flowers heterostylous (? always), hermaphrodite or rarely unisexual, in tight capitula, the flowers usually joined, at least by the bases of the calyces, the capitula sometimes bearing single large coloured bracts or occasionally many smaller bracts; capitula 1-several at the nodes, frequently arranged in umbels, pedunculate or rarely sessile.
Ovary 2–4-locular, sometimes imperfectly so; style with 2 short to long linear branches; ovules solitary in the locules, attached to the septum below the middle or near the base, ascending, anatropous or amphitropous.
Fruit syncarpous (very rarely scarcely so), succulent, containing several pyrenes; pyrenes cartilaginous or bony, 1-seeded or joined into a 2–4-locular woody structure.
Calyx tube urceolate or hemispherical, the limb short, truncate or obscurely to distinctly toothed, persistent.
Corolla ± coriaceous, funnel-shaped or salver-shaped; lobes (4)5(7), valvate; throat glabrous or pilose.
Stamens (4)5(7), inserted in the throat; filaments short; anthers and style included or exserted.
Trees, shrubs or less often lianes, with mostly glabrous, less often hairy or tomentose stems.
Leaves opposite or rarely in whorls of 3, sometimes only 1 at flowering nodes.
Seeds obovoid or reniform, with a membranous testa and fleshy endosperm.
Stipules leafy, undivided, free or forming a sheath with the petioles.
Disk swollen or annular.