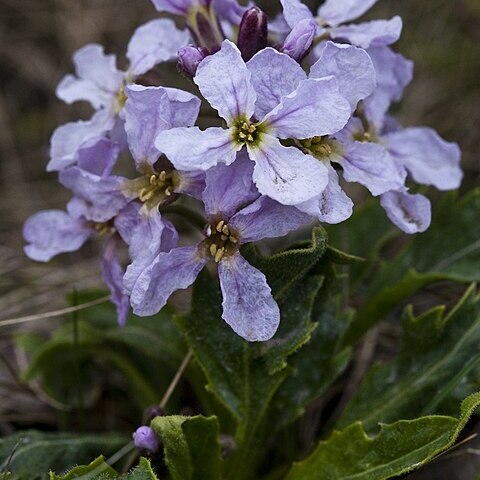
Herbs perennial, with well-developed caudex, rarely subshrubs or shrubs. Trichomes simple or absent, multicellular glands present or absent. Stems leafy or leafless. Basal leaves petiolate, rosulate, simple, entire, dentate, or pinnately dissected. Cauline leaves similar to basal, often absent. Racemes ebracteate, elongated in fruit. Fruiting pedicels erect, ascending, or divaricate. Sepals linear or oblong, caducous, erect, unequal, base of lateral pair saccate, margin membranous. Petals purple, pink, or white; blade obovate, apex rounded or emarginate; claw subequaling or longer than sepals. Stamens 6, tetradynamous; filaments dilated or not at base; anthers oblong or linear, obtuse at apex. Nectar glands 2, lateral, annular to semiannular; median glands absent. Ovules 10-50 per ovary. Fruit dehiscent siliques, linear, oblong, or lanceolate, strongly latiseptate or rarely subterete or 4-angled, sessile or subsessile, persistently attached to pedicel, unsegmented; valves leathery, with a prominent midvein and obscure to distinct lateral and marginal veins, smooth or torulose; replum almost always flattened; septum complete, membranous or thickened, translucent or opaque; style distinct, 0.5-7 mm; stigma conical or cylindric, 2-lobed, lobes prominent, connate, decurrent. Seeds uniseriate, often broadly winged, suborbicular or oblong, strongly flattened; seed coat smooth, not mucilaginous when wetted; cotyledons accumbent.