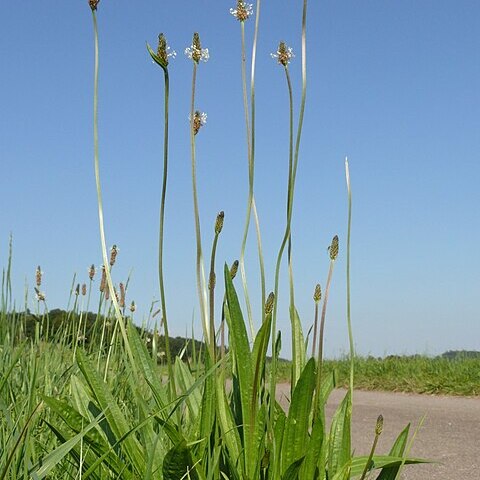
Animal or perennial, terrestrial or, in one small genus, aquatic herbs. Leaves mostly spirally arranged and all radical, less often cauline, alternate or opposite, simple, often sheathing at the base, sometimes reduced, exstipulate. Flowers small, hermaphrodite, or in one small genus unisexual, regular, sessile in the bract-axils, forming axillary spikes or capitate racemes. Calyx herbaceous, 4-lobed, the lobes ± free or sometimes the lower pair ± united. Corolla gamopetalous, scarious, 3-4-lobed, the lobes imbricate. Stamens (l-2-)4, inserted in the corolla-tube and alternating with the lobes, rarely hypogynous; filaments usually long; anthers versatile, 2-thecous, the thecae opening lengthwise. Ovary superior, 1-4-locular; style long, simple, often exserted; ovules l-? in each locule, axile or basal. Fruit a membranous circumscissile capsule or a 1-seeded bony nut. Seeds peltately attached, often sticky when wet; embryo straight, rarely curved, placed in the middle of the fleshy endosperm
Herbs or small shrubs, rarely arborescent. Stipules absent. Leaves spirally alternate, usually in a basal rosette, rarely opposite or whorled, simple; leaf blade veins (1 or)3-11, arcuate. Inflorescences spikes, rarely racemes or 1-flowered, pedunculate, each flower with 1 bract. Flowers small, protogynous, bisexual, rarely polygamous or unisexual. Calyx usually 4-parted, persistent, segments imbricate. Corolla scarious or membranous, gamopetalous, actinomorphic or rarely zygomorphic, (3 or)4-lobed; lobes imbricate. Stamens (1 or 2 or)4, inserted on corolla tube, alternate with lobes; anthers free, versatile, with an apical appendage, thecae 2 and parallel. Pistil consisting of 2 carpels; ovary superior, (1 or)2-loculed, axile or rarely basal; style 1, filiform, mostly longitudinally stigmatic. Fruit a pyxis, rarely an indehiscent capsule or nutlet, with 1 to numerous seeds. Seeds minute; cotyledons narrow; endosperm fleshy.
Stamens (1–2) 4, inserted in the corolla tube and alternating with the leaves, rarely hypogynous, usually exserted; filaments usually long, filiform; anthers versatile, 2-thecous, the thecae dehiscing longitudinally
Leaves mostly spirally arranged and all radical, less often cauline and spiral, alternate or opposite, simple, often sheathing at the base, sometimes reduced, exstipulate
Ovary superior, 1–4-locular, with 1-many ovules in each locule, axile or basal; style single, long, usually filiform, simple, often exserted
Flowers small, hermaphrodite or unisexual (not in Flora Zambesiaca area), usually 4-merous, actinomorphic or rarely so, sessile, bracteate
Stamens usually 4, inserted on the corolla-tube and alternate with the lobes or hypogynous; anthers 2-celled, opening lengthwise
Seeds peltately attached, often mucilaginous when wet, 1-many; embryo straight, rarely curved, enclosed by the fleshy endosperm
Calyx herbaceous, persistent, 4-lobed, the lobes more or less free or sometimes the lower pair more or less united
Inflorescence usually a spike, rarely capitate racemes, terminating a scape. Each flower subtended by a bract
Corolla gamopetalous, scarious, 3–4 lobed; tube ampulliform or cylindric, lobes imbricate, equal, spreading
Annual or perennial, terrestrial or aquatic (not in Flora Zambesiaca area) herbs
Seeds peltately attached, with fleshy endosperm and straight or curved embryo
Leaves all radical or alternate or opposite, simple, sometimes much reduced
Fruit a capsule, membranous, circumscissile or 1-seeded, hard, indehiscent
Corolla gamopetalous, scarious, 3-4-lobed, lobes imbricate
Flowers usually hermaphrodite, spicate, actinomorphic
Ovules 1 or more in each cell, axile or basal
Ovary superior, 1-4-celled; style simple
Fruit a circumscissile capsule or nut
Calyx herbaceous
Herbs