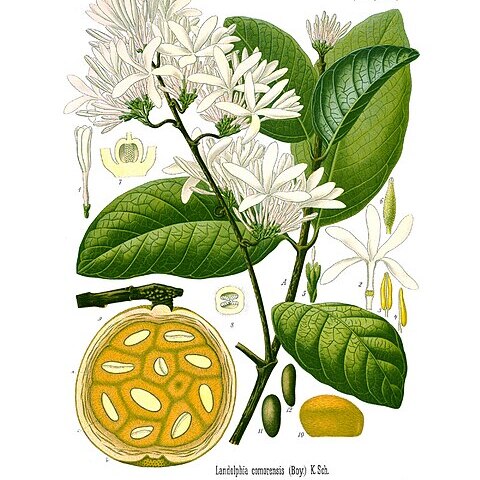
A creeper or vine. It grows 30-40 m long. It can be 1.9 m around. The stems are purplish-red. It has white milky sap. The leaf blade is 7-20 cm long by 4-10 cm wide. They are oval. It often has tendrils. The flowers are large and white. They have a sweet scent. They are in large groups at the ends of branches. The fruit are round and 6 cm across. They are yellow or orange. The fruit are edible. The shell is hard and bitter. The pulp is soft and reddish. It contains seeds.
Corolla tube 18–24 mm. long, slender, slightly inflated just below the middle, outer surface completely glabrous or pubescent, especially towards the apex, inner surface pilose; corolla lobes 16–30 x 3–9 mm., oblong-elliptic or obovate-elliptic, rounded at apex, minutely and irregularly ciliate, lower surface glabrous or pubescent towards the base, upper surface glabrous or shortly pilose near the base.
Leaves membranous, not strongly discolorous; petiole 8–14 mm. long, glabrous; lamina 7–19·5 x 4–9·5 cm., elliptic or ovate, rounded or obtuse at apex, rounded to subcordate at base; both surfaces glabrous, with lateral and tertiary nerves in relief; midrib raised below, impressed, level or slightly raised above; vein reticulation weakly scalariform.
Calyx 2·5–3 mm. long, lobes strongly imbricate, free to base, oblong, rounded at apex, dorsally glabrous or tomentose, minutely ciliate.
Inflorescences terminal many-flowered paniculate cymes, forming large dense heads or lax and tendrillous; axes glabrous or tomentose.
Ovary subglobose, c. 1 mm. long, with a ring of stiff erect hairs at the apex; style, clavuncle and stigma 4–5 mm. long.
Vigorous liane climbing to 30 m.; stem terete, slash pink with white milky sap, bark brown, almost smooth.
Fruit globose, up to 6 cm. in diameter when ripe, yellow or orange with white or orange pulp, edible.
Stamens inserted just below the middle of the corolla tube; anthers c. 2·75 mm. long, subsessile.
Young branches glabrous, lenticels conspicuous, small, circular, light-coloured, numerous.
Flowers large, white, attractive, very sweet-scented.
Tendrils common.