Perennial herbs with annual leaves and flowers. Dormant in summer. Corm globose; tunic fibrous. Leaves mostly basal, linear to lanceolate, flat, soft-textured, with prominent midveins. Scape unbranched or few-branched, with up to 2 cauline leaves. Spike distichous to secund, lax, few-flowered. Bracts lacerate, scarious, brown-streaked. Flowers erect, actinomorphic or slightly zygomorphic. Perianth tube straight, funnel-shaped; lobes erect to spreading, equal, longer than tube. Stamens equilateral to unilateral; anthers basifixed. Style branches 3, filiform or cuneate, entire. Capsules obloid, thin-walled. Seeds numerous, globose, smooth. Bulbils often produced in leaf axils after flowering. [This description from Cooke (1986: 56) requires revision, it excluded Synnotia (Cooke 1986: 57–58) which has since been treated as a synonym of Sparaxis-Editor, 29 September 2020.]
Small perennial herbs with annual leaves and flowers. Corm globose; tunic fibrous. Leaves mostly basal, lanceolate to ensiform, flat, soft-textured, with prominent midvein. Stem erect, unbranched or few-branched. Spike distichous, few-flowered, lax. Bracts ovate, dentate to lacerate, scarious, brown-streaked. Flowers zygomorphic, bilabiate. Perianth tube curved, funnel-shaped; lobes unequal; dorsal lobe largest, erect; lateral lobes spreading; lower 3 lobes connivent, forming a projecting lip. Stamens unilateral, arched under dorsal lobe. Style arched, branches 3, entire, short, expanded at apices. Capsules obloid. Seeds globose, smooth.
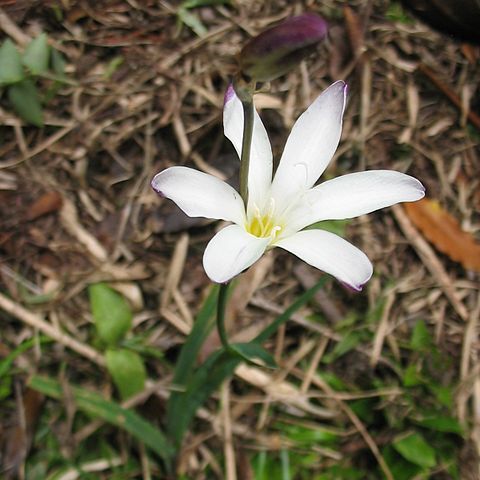
Summer-green, grass-like perennial. Corm small, globose; tunic fibrous. Leaves basal and distichous, a few cauline; cormils sometimes in leaf-axils. Inflorescence simple or branched, few-flowered. Flowers large, cream or brightly coloured, actinomorphic or sub-zygomorphic, each within 2 dry, scarious, usually lacerate spathe-valves; tube short, straight, cylindrical below, funnel-shaped above; lobes ± equal, > tube. Stamens asymmetric or symmetrical. Style-branches 3, entire. Capsule globose, firmly membranous. Seeds many, globose. Spp. 6, all of S. Africa. Adventive spp. 2.