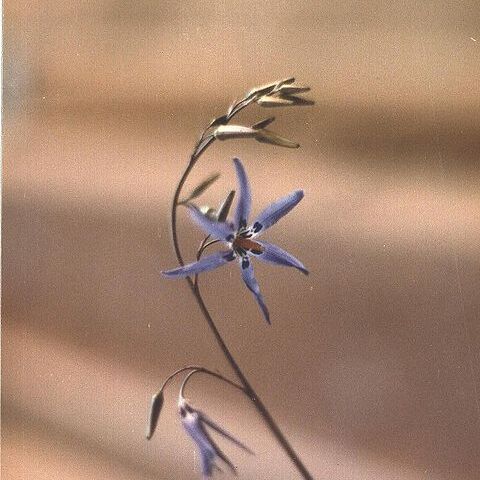
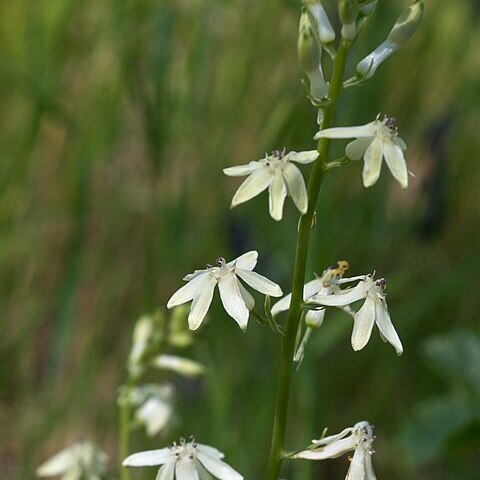
Perennial herbs with corms or tubers. Leaves petiolate, sessile or amplexicaul, linear to ovate-orbicular, decurrent to cordate. Inflorescence racemose, pseudo-racemose or paniculate, or the flowers solitary. Bracts sometimes minute or absent. Flowers pedicellate, hermaphrodite, regular or slightly irregular. Perianth-segments 6, free or forming a short tube, entire, spreading or reflexed. Stamens 6, inserted on the perianth-segments at the throat of the tube, all perfect or 2 or 3 replaced by linear staminodes; anthers dithecous, sometimes connivent, with the base sometimes produced into a spur or sac; dehiscence by an apical pore, usually slightly introrse. Ovary semi-inferior, rarely almost superior, trilocular; ovules 2–? in each cell; placentation axile; style filiform; stigma minutely trifid. Capsule trilobed, dehiscence loculicidal; seeds small and numerous, or a few large ones, rarely only one developing, smooth or warted, rarely with spongy cap; endosperm present
Perianth-tube short or absent; lobes 6, spreading or reflexed, subequal, imbricate Stamens 6, perfect, or 3 and with 3 staminodes, inserted at the throat of the perianth; anthers 2-locular, the connective often produced at both ends, the base then swollen or spur-like, cells opening by a terminal pore, rarely by a slit
Stamens 6, inserted at the throat of the perianth tube, equal (or in the New World sometimes heteromorphic or some reduced to staminodes); filaments glabrous, short; anthers basifixed, 2-locular, sometimes tailed, connivent at apex or not, dehiscing by an apical pore or clavate slit, or splitting longitudinally
Inflorescences terminal in acaulescent plants, or lateral on caulescent plants, scapose or pedunculate; flowers in panicles, racemes or spikes, or flowers solitary, usually bracteate, leaves and scape sometimes arising separately from each other on the corm apex
Leaves basal or cauline, spirally arranged, sessile or ± petiolate, sheathing or not at the base, entire, linear or lanceolate to ovate; the outer leaves reduced to ± membranous non-photosynthetic sheaths without blades (cataphylls)
Glabrous geophytic herbs, perennating from corms or tubers; corms with or without a fibrous tunic of persistent sheathing leaves or leaf remnants (tunic absent in the Flora Zambesiaca area)
Flowers bisexual, actinomorphic, in simple racemes separately from the tuber or corm, or in panicles; bracts large and membranous to small
Capsule 3-lobed, loculicidal; seeds small numerous smooth or warty, or few and large and sometimes with a conspicuous chalazosperm
Perianth segments (tepals) 6, fused into a short tube at the base, or ± free to the base, segments reflexed or not
Leaves radical or towards the base of the flowering stems, linear to ovate-orbicular and cordate, glabrous
Ovary inferior, semi-superior or superior, 3-locular; placentation axile, ovules 2-many per carpel
Style erect, filiform, straight or curved; stigma small, capitate or minutely 3-fid
Herbs with fibrous tunicated corms or thick orbicular flattened tubers
Flowers hypogynous, bisexual, trimerous, actinomorphic, pedicellate
Ovary semi-inferior, 3-locular; style subulate or filiform
Ovules numerous, axile, 2-seriate in each loculus
Seeds numerous, with fleshy endosperm
Fruit a loculicidal capsule
Caulescent or acaulescent