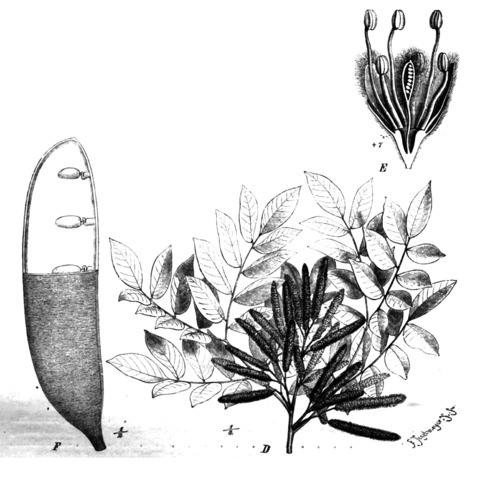
Unarmed trees. Leaves bipinnate, with 2-5 pairs of pinnae; stipules small, deciduous; leaflets alternate, petiolate, eglandular. Inflorescences of pedunculate spike-like racemes usually ±aggregated into panicles; bracts small, falling as or before the flowers open. Flowers bisexual. Calyx lobes 5, ±united below or almost free to the base, slightly imbricate but open from an early stage. Petals 5, equal, free, ±imbricate. Stamens 10, often alternately longer and shorter; filaments free; anthers dorsifixed. Ovary stipitate, tapering into a narrowly conical style; stigma minute, punctiform, minutely ciliolate. Pod ±oblong, flattened, straight or slightly curved, coriaceous to woody, dehiscing along one or both margins. Seeds without areoles, flattened, transverse in the pod.
Trees. Leaves alternate, bipinnate; stipules caducous, small; pinnae few pairs, opposite; leaflets alternate, leathery. Flowers small, crowded together in terminal panicles of spicate racemes. Calyx campanulate, with 5 short subequal lobes; tube short. Petals 5, subequal. Stamens 10, free; filaments equal or alternately longer and shorter. Ovary stalked, hairy; ovules numerous; style short; stigma small. Legume compressed, long, thickly leathery, 2-valved dehiscent when ripe, pulpy within between seeds. Seeds transverse, oblong or obovoid, compressed, with endosperm.
Inflorescences of dense spike-like racemes of small ± contiguous flowers (similar in appearance to those of many genera of Mimosoideae), usually ± aggregated into panicles; bracts very small, falling as or before the flowers open.
Leaves bipinnate with 2–5 pairs of pinnae, without specialised glands on petiole and rachis; leaflets up to 17 per pinna, alternate, eglandular, petiolulate; stipules very small and quickly falling.
Stamens 10, often alternately longer and shorter; filaments glabrous or hairy; anthers dorsifixed, dehiscing by longitudinal slits; connective not projecting beyond the anther.
Ovary shortly stipitate, pubescent to tomentose, with several ovules, tapering into a narrowly conical style; stigma minute, punctiform, cup-shaped and minutely ciliate.
Pods stipitate, ± oblong, straight or curved, coriaceous to woody, dehiscing along one or both margins; seeds up to 11, compressed, not areolate, with endosperm.
Sepals 5, connate in their lower part or almost free to the base, slightly imbricate but open from an early stage.
Petals 5, equal, free, ± imbricate, pubescent, oblong to oblanceolate-spathulate.
Flowers hermaphrodite.
Unarmed trees.